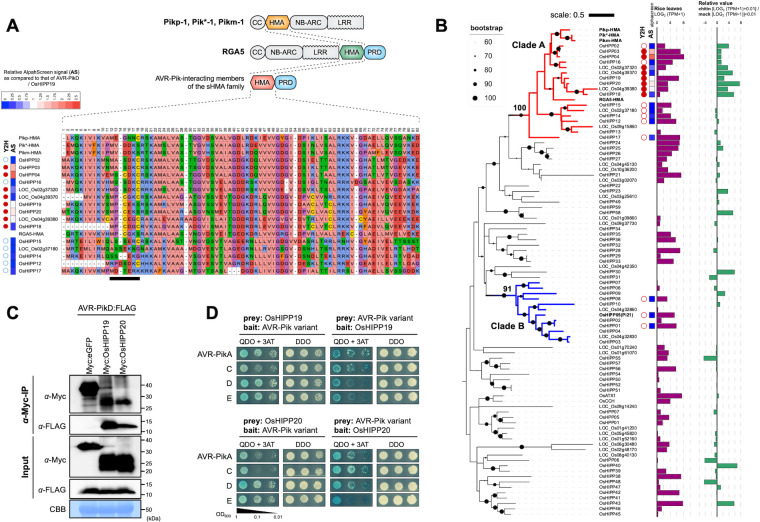
Fig 1. AVR-PikD binds Clade A sHMAs.
(A) Schematic representation of the Pik-1 (Pikp-1, Pik*-1, Pikm-1) and RGA5 Nucleotide-binding Leucine Rich Repeat Receptors (NLRs) and small HMA (sHMA) proteins of rice. CC: coiled-coil domain; NB-ARC: nucleotide binding domain; LRR: leucine rich repeat; PRD: proline-rich domain. Amino acid sequence alignment of a subset of HMA proteins of rice. The black bar highlights the putative metal-binding motif MxCxxC. Interaction with AVR-PikD is indicated for yeast two-hybrid (Y2H: red dot: binding; white dot: non-binding) and AlphaScreen (AlphaScreen Signal [AS]: strength of interaction signal as compared to that of AVR-PikD/OsHIPP19 interaction is given in the inset). (B) A maximum likelihood tree of the HMA domains of 87 sHMA of rice. Amino acid sequences of the HMA domains were aligned and used for reconstruction of the phylogenetic tree. The dots on the branches indicate bootstrap values after 1,000 replications. Clade A and Clade B are indicated by red and blue branches, respectively. Note Pi21 (OsHIPP05) belongs to Clade B. Y2H and AlphaScreen results (AS) are as shown as in (A). Bar graphs in purple color show expression level of each gene in leaves as revealed by RNA-seq (log2(TPM+1) value). Bar graphs in green color show the induction level of each gene in rice suspension cultured cells after chitin treatment (log2[TPM of chitin-treated cultured cells+1] + 0.01)/ (log2[TPM of mock-treated cultured cells+1] + 0.01). (C) Results of co-immunoprecipitation of AVR-PikD with OsHIPP19 and OsHIPP20 transiently expressed in Nicotiana benthamiana leaves. (D) Y2H interactions of the AVR-Pik variants, AVR-PikA, AVR-PikC, AVR-PikD, AVR-PikE, to OsHIPP19 and OsHIPP20.