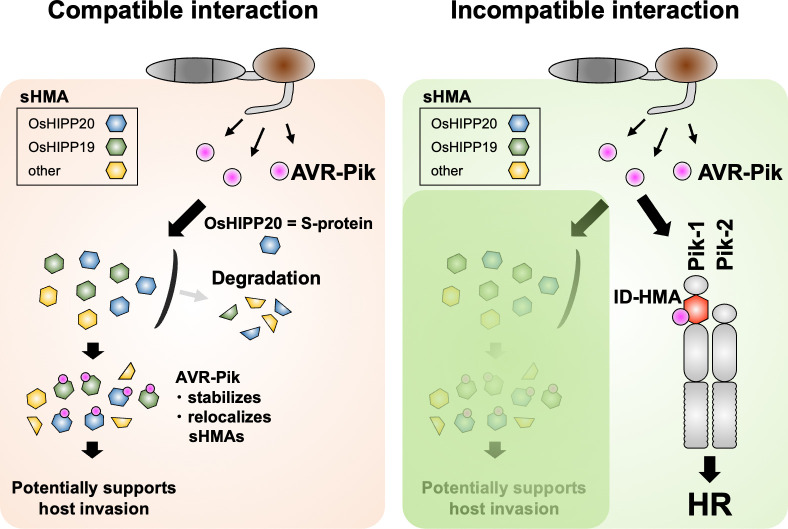
Fig 5. Schematic representation of a model showing molecular interactions between the AVR-Pik effector, rice sHMA proteins and Pik NLRs.
In the compatible interaction (susceptible, left), AVR-Pik binds rice Clade A sHMA proteins, stabilizes and relocalizes them, possibly enhancing pathogen virulence. OsHIPP20 is a S-protein required for effective M. oryzae invasion. In the incompatible interaction (resistant, right), AVR-Pik interacts with integrated HMA domains of the Pik-1 NLRs which, together with Pik-2, triggers disease resistance by the hypersensitive response (HR). AVR-Pik and Pik seem involved in arms-race coevolution (selective force to enhancing interaction in Pik and evading interaction in AVR-Pik) by each generating multiple variants.