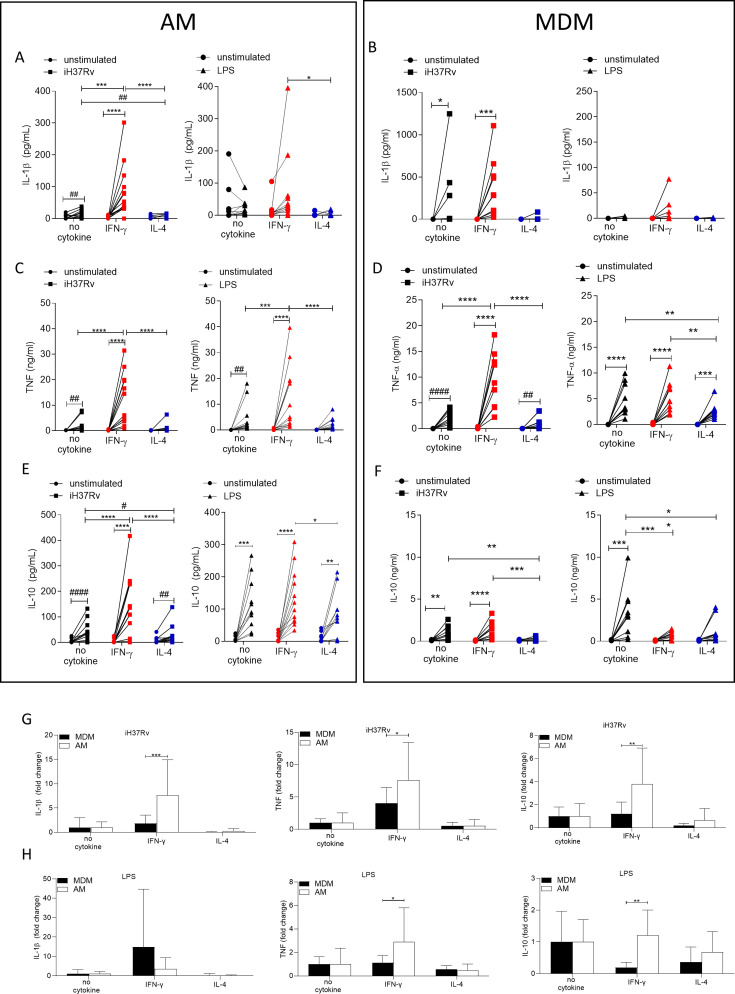
Figure 4. IFN-γ enhances cytokine production more in AM compared with MDM.
Human AM (A, C, E) isolated from bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. PBMC were isolated from buffy coats and MDM (B, D, F) were differentiated and adherence purified for 7 days in 10% human serum. Cells were left unprimed (black) or primed with IFN-γ (red) or IL-4 (blue) (both 10 ng/ml) for 24 hr. AM or MDM were left unstimulated (circle) or stimulated iH37Rv (MOI 1–10; square) or LPS (100 ng/ml; triangle). Supernatants were harvested 24 hr after stimulation and concentrations of IL-1β (A, B), TNF (C, D), and IL-10 (E, F) were quantified by ELISA. Fold change in IL-1β, TNF and IL-10 was calculated for AM and MDM based on the average of respective no cytokine controls for iH37Rv (G) and LPS (H). Each linked data point represents the average of technical duplicates for one individual biological donor (AM; n=12–13, MDM; n=8–10). Statistically significant differences were determined using two-way ANOVA with a Tukey (A–F) or Bonferroni post-test (G–H); *p≤0.05, **p≤0.01, ***p≤0.001, ****p≤0.0001 or #p≤0.05, ##p≤0.01, ####p≤0.0001 (where IFN-γ-treated data sets were excluded for post-test analysis to analyse statistical differences between no cytokine and IL-4-treated data sets).