Figure 5.
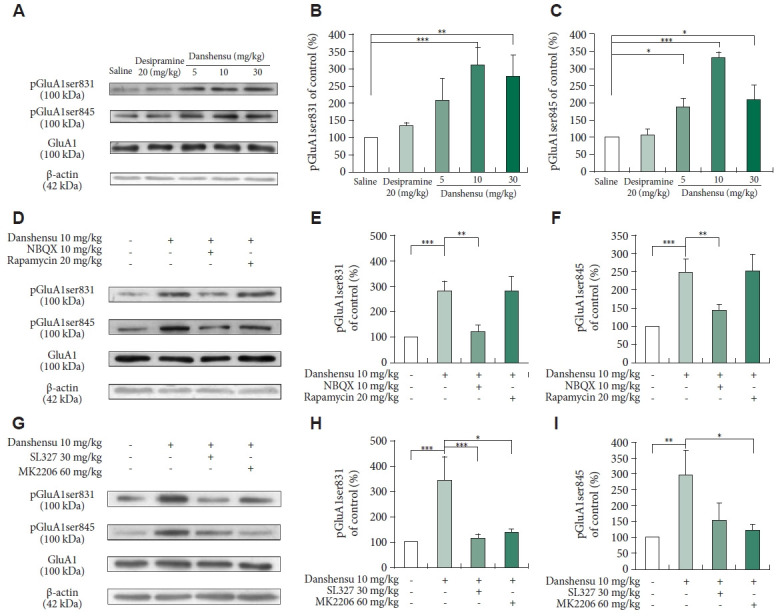
Post-treatment changes in the levels of phosphorylated GluA1ser845 and GluA1ser831. We evaluated the activation of GluA1ser845 and GluA1ser831 in the hippocampus of mice treated with saline, desipramine (20 mg/kg), or danshensu (5, 10, or 30 mg/kg). Western blotting was performed to measure the levels of phosphorylated GluA1ser845 and GluA1ser831 in mice treated with 10 mg/kg danshensu (A), those pretreated with NBQX (10 mg/kg) or rapamycin (20 mg/kg) (D), and those pretreated with SL327 (30 mg/kg) or MK2206 (60 mg/kg) (G). Treatment with 10 and 30 mg/kg danshensu significantly promoted the activation of GluA1ser831 (B) and GluA1ser845 (C). Densitometric analyses of the blots (normalized to β-actin levels) revealed that the levels of phosphorylated pGluA1ser831 (E) and pGluA1ser845 (F) were increased in mice treated with danshensu; these increases were blocked by pretreatment with NBQX but not rapamycin (D-F). Notably, pretreatment with SL327 or MK2206 block the danshensu-induced increase in the level of phosphorylated GluA1ser845 or GluA1ser831 (G-I). N=4 per group. Between-group comparisons were performed using the nonparametric Kruskal–Wallis test, followed by the Conover–Iman post hoc test. Data are presented in terms of the mean±standard error of the mean values. *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001. GluA1, glutamate A1 subunit of AMPAR; AMPAR, α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor; NBQX, 2,3-dioxo-6-nitro- 7-sulfamoyl-benzo(f)quinoxaline.
