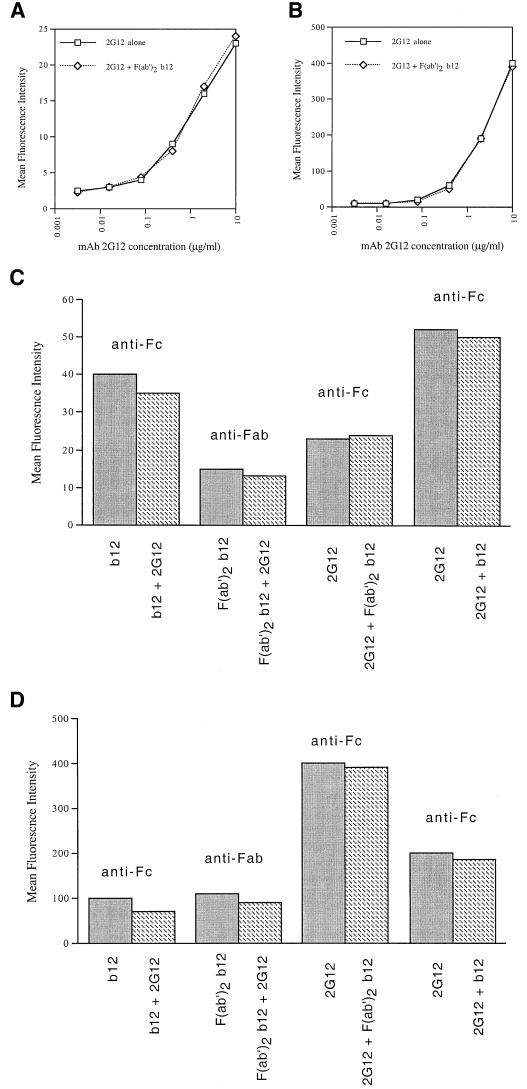
FIG. 1.
Analysis of cooperativity of MAb binding to HIV-1 envelope spikes. Binding of MAb 2G12 to HIV-1 envelope expressed on the surface of HIV-1HxB2-infected H9 cells (A) or BHK cells infected with a recombinant vaccinia virus expressing HIV-189.6 envelope (B) was detected by using flow cytometry. Dose-response curves of MAb 2G12 binding were assessed in the absence or presence of a subsaturating amount of F(ab′)2 fragments of MAb b12. Detection of bound antibody was performed with a fluorochrome-labeled antibody against Fc (A and B). (C and D) Binding of MAb b12, MAb 2G12, and F(ab′)2 b12 and their combinations to HIV-1HxB2-infected H9 cells and BHK cells infected with a recombinant vaccinia virus expressing HIV-189.6 envelope, respectively. Antibody binding was detected with a fluorochrome-labeled antibody against the Fc or Fab fragment as indicated above the bars. The primary antibody (dark bars, or indicated first in the antibody pair described below the hatched bars) was tested at 10 μg/ml, whereas the secondary antibody (shown as the second antibody below the hatched bars) was tested at a subsaturating concentration (resulting in 50 to 75% of maximal binding). The results in the third pair of bars correspond to the data in panels A and B and are shown for comparison.