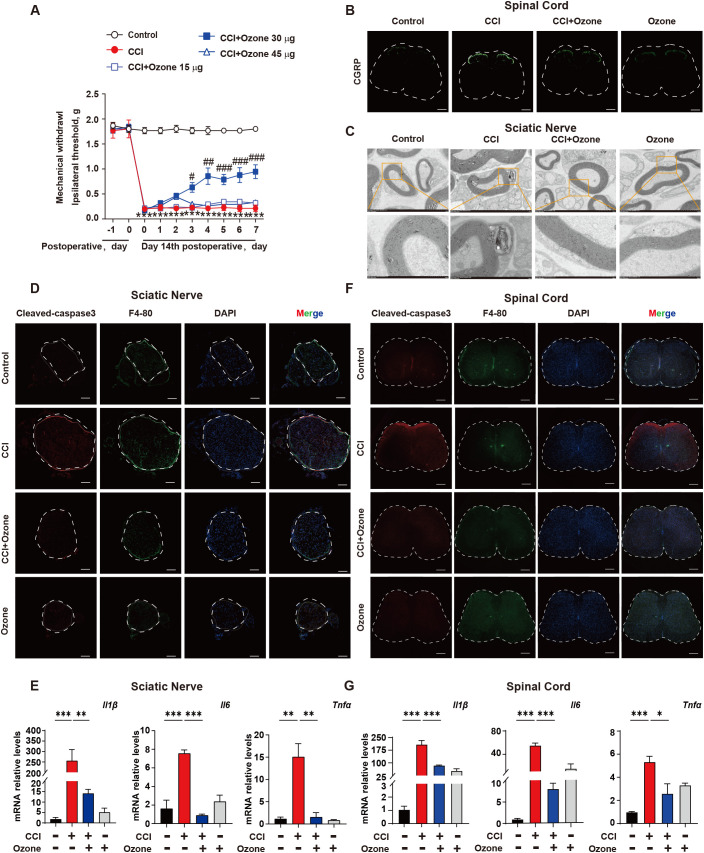
Figure 2.
Ozone decreases the accumulation of apoptotic cells and suppresses neuroinflammatory responses to treat NPP. (A) On the 14th day after establishing the CCI mouse model, mice were exposed to ozone at different concentrations for 7 days, and the effect of ozone on the mechanical pain threshold of CCI mice was evaluated (n=6). (B) On the 7th day of ozone treatment, the content of c-GRP in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord was detected (n=3), Scale bars, 200μm; mouse sciatic nerves were collected to investigate the effect of ozone on the demyelination response in CCI mice (n=3) (C). (D) Apoptotic cell accumulation in the sciatic nerves among different treatment groups was examined (n=3). Scale bars, 100μm. (E) Transcription levels of inflammatory factors in mouse sciatic nerves were assessed (n=3). (F, G) The effect of ozone on apoptotic cells in the spinal cord of CCI mice and the impact on transcription levels of inflammatory factors were examined (n=3). Scale bars, 200μm. Significant differences were revealed following one-way ANOVA (E, G) or two-way ANOVA (A) (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001; #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, and ###p < 0.001 vs. CCI).