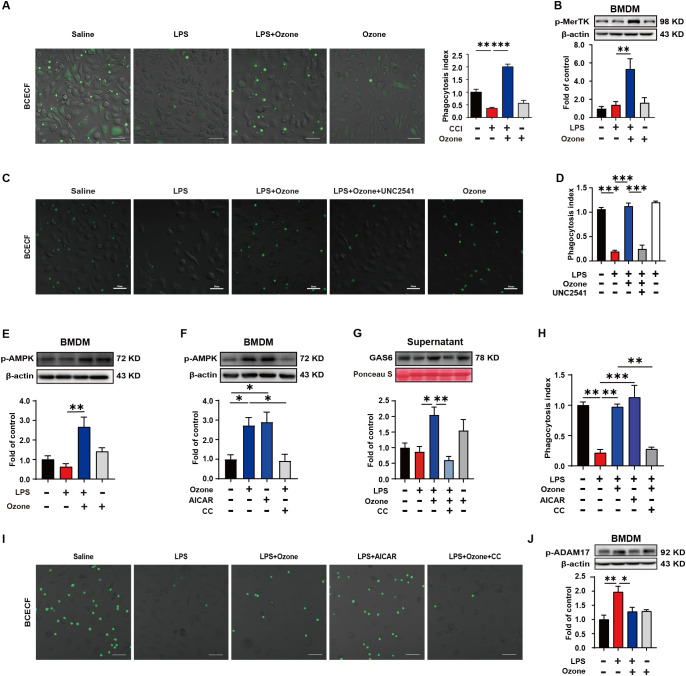
Figure 3.
Ozone promotes macrophage efferocytosis of apoptotic cells through the activation of AMPK/gas6/MerTK pathway. (A) BMDMs from WT mice were stimulated with LPS (1μg/ml) for 6 hours to establish an inflammatory model and exposed to ozone (30μg/ml) for 4 hours. The engulfment of apoptotic neutrophils by BMDMs was evaluated (n=3). Scale bars, 50μm. (B) Whole-cell lysates of BMDMs were collected to examine the expression level of p-MerTK (n=3). (C, D) BMDMs were stimulated with LPS (1μg/ml) for 6 hours to establish an inflammatory model and pretreated with a MerTK receptor inhibitor UNC2541 (2.5mM) for 30 minutes, followed by treatment with ozone (30μg/ml) for 4 hours. The engulfment of apoptotic neutrophils by BMDMs was evaluated (n=3). Scale bars, 50μm. (E, F) Whole-cell lysates of BMDMs were collected to detect the expression level of p-AMPK and BMDMs were stimulated with an AMPK inhibitor CC (20μM) for 15 minutes to investigate its effect on ozone-induced AMPK activation (n=3). (G) Supernatants of BMDMs were collected to measure the secretion of Gas6 in different treatment groups (n=3). (H, I) BMDMs were stimulated with LPS (1μg/ml) for 6 hours to establish an inflammatory model and pretreated with AICAR (300μM) or CC (20μM) for 15 minutes, followed by treatment with ozone (30μg/ml) for 4 hours. The engulfment of apoptotic neutrophils by BMDMs was evaluated (n=3). Scale bars, 50μm. (J) The expression level of p-ADAM17 of BMDM was detected (n=3). Significant differences were revealed following one-way ANOVA (B, D, E-H, J) (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001).