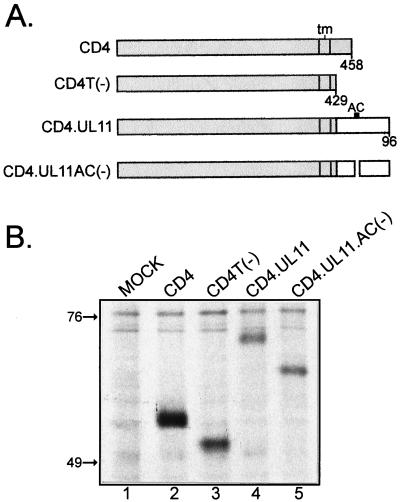
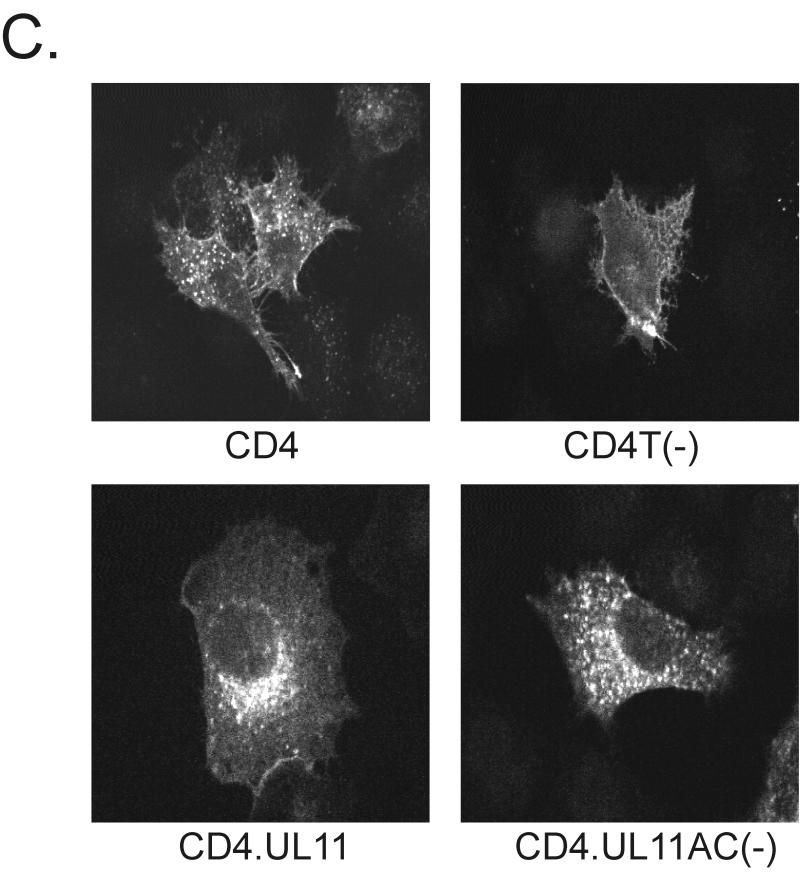
FIG. 3.
Recovery of CD4-UL11 chimeras from the plasma membrane. (A) CD4-UL11 constructs. The 458-amino-acid human CD4 protein (shaded rectangle) contains a large extracellular domain, a hydrophobic transmembrane domain (tm), and a short cytoplasmic domain. The wild-type UL11 sequence or the acidic cluster (AC) deletion mutant (open rectangles) was attached to the CD4 protein in place of the last 29 residues of the cytoplasmic tail, but in this case, GFP was not included. (B) Biochemical analysis. A7 cells were transfected and metabolically labeled with [35S]methionine for 2.5 h. The CD4 derivatives were immunoprecipitated with a monoclonal antibody specific for CD4, separated by SDS-PAGE, and visualized by autoradiography. The positions of molecular mass markers (in kilodaltons) are indicated. (C) Subcellular localization. A7 cells transfected with the indicated constructs were incubated with a monoclonal antibody specific for CD4 for 40 min on ice. After excess antibody was washed away, the cells were shifted to 37°C for 60 min to allow for endocytosis. To detect internalized antibody, the cells were fixed, permeabilized, stained with fluorescein isothiocyanate-labeled secondary antibody, and visualized by confocal microscopy.