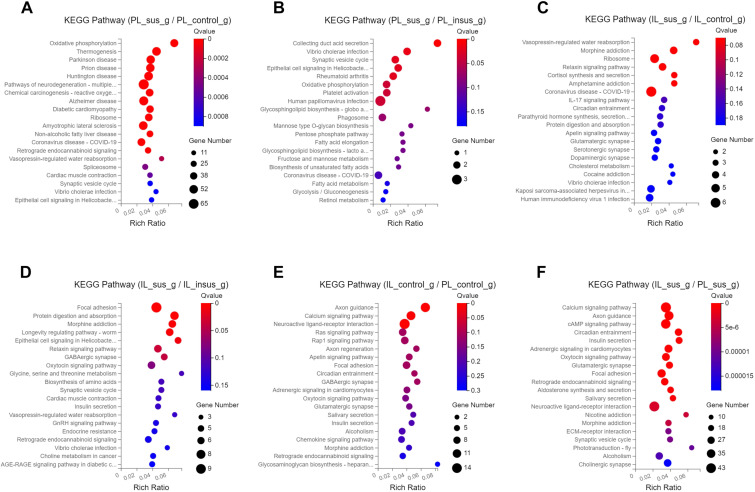
Figure 3.
Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathways impacted by single prolonged stress (SPS). (A) DEGs in the PL-susceptible group, compared to the PL-control group, reveal an enrichment of KEGG pathways related to Parkinson’s, Huntington’s, and Alzheimer’s diseases, as well as pathways involved in neurodegeneration. (B) DEGs in the PL-susceptible group show less KEGG pathway enrichment when compared to the PL-insusceptible group. (C, D) In contrast to the IL-control and IL-insusceptible groups, the IL-susceptible group presents significant KEGG pathway enrichment associated with addiction-like behaviors, such as morphine and amphetamine addiction. Focal adhesion and relaxin signaling pathways are also more enriched in DEGs. (E) DEGs of PL and IL-control groups are involved in axon guidance, calcium signaling pathways, and neuroactive ligand-receptor interactions. (F) KEGG pathways affected by SPS in both PL-susceptible and IL-susceptible groups. Note: The X-axis represents the enrichment ratio (calculated as Rich Ratio = Term Candidate Gene Num/Term Gene Num), while the Y-axis denotes the KEGG pathway. Bubble size indicates the number of genes annotated to the KEGG pathway, and color represents enriched significance. The redder the color, the smaller the significance value (n=4 in each group).