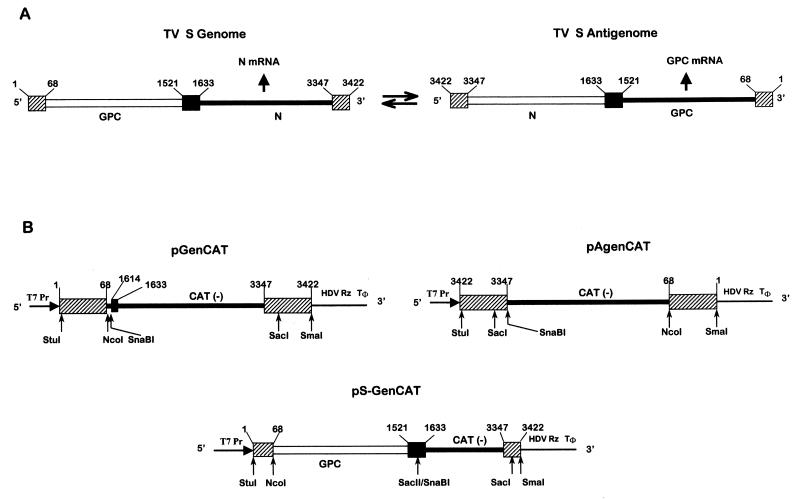
FIG. 1.
Schematic diagram (not to scale) showing the TV S RNA organization and expression (arrows show the direction of RNA synthesis) (A) and plasmids used to generate TV RNA analogs (B). The position of T7 polymerase promoter (T7Pr), the HDV Rz, and the T7 RNA polymerase terminator (Tφ) are indicated. Constructions were performed as indicated in Materials and Methods. pGenCAT transcript (842 nt) contains (5′ to 3′) the entire TV S genome 5′ NCR sequence (68 nt), a short linker (16 nt) including a SnaBI site, a short sequence (nt 1614 to 1633) of the S genome intergenic region (IGR) which is not involved in the hairpin structure (18), CAT ORF in an antisense orientation (660 nt), and the complete S genome 3′ NCR sequence (76 nt). pAgenCAT transcript (810 nt) contains (5′ to 3′) the entire TV S antigenome 5′ NCR sequence, a SnaBI site, CAT ORF in an antisense orientation, and the complete S antigenome 3′ NCR. pS-GenCAT (2,343 nt), contains (5′ to 3′) nt 1 to 1633 of the TV S genome followed by the negative-sense copy of CAT and the entire S genome 3′ NCR sequence. Sizes of transcripts refer to the processed RNA, which includes two nonviral Gs at the 5′ end (23). Nucleotides were numbered considering as 1 the 5′ end of the S genome. Open lines represent positive-sense coding regions; negative-sense coding regions are indicated in blackened thicker lines. S RNA IGR is represented as a black box, and the 3′ and 5′ NCR termini are indicated as shaded boxes. Key restriction endonuclease sites used in the assembly of the DNA constructs are shown.