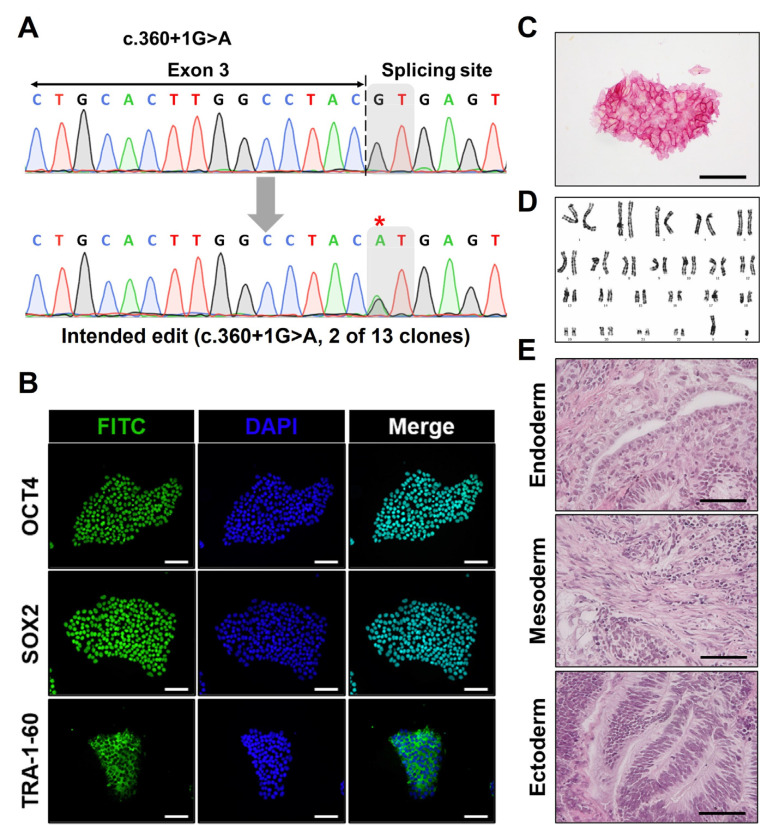
Fig. 4.
Generation and characterization of an isogenic human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSC) line with intended ENG mutation by prime editing. (A) Single-cell colonies were formed and expanded. Genomic DNA samples of each colony were amplified by polymerase chain reaction (PCR). After sequencing the PCR products, the results were analyzed to investigate the genotype of each colony. Among 13 acquired clones, two clones possessed the intended mutation (ENG c.360+1G>A) heterozygously. The asterisk mark indicates the target base pair. (B, C) Immunofluorescence staining and AP staining were performed to evaluate the pluripotency of generated isogenic mutant hiPSC line (scale bar=100 μm). (D) Chromosomal integrity was confirmed by karyotyping. (E) Teratoma assay was further conducted to verify in vivo pluripotency, resulting in the formation of all three germ layers including endoderm, mesoderm, and ectoderm (scale bar=50 μm).