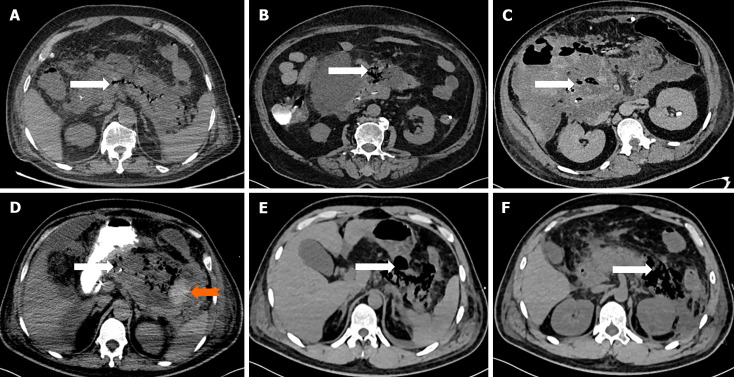
Figure 2.
Computed tomography imaging findings in patients with hyperematous pancreatitis. A: Computed tomography (CT) scan showing gas confined to the pancreatic parenchyma (white arrow) with pancreatic swelling; B: Gas confined to the body of the pancreas (white arrow) with significant swelling of the pancreatic head; C: Gas confined to the pancreatic head (white arrow) with multiple gas cavities and exudate involving the right hepatorenal space; D: Gas confined to the body and tail of the pancreas (orange arrow) with haemorrhage in the pancreatic tail (broad white arrow) and exudate involving the perisplenic and perirenal areas; E: Gas confined to the body and tail of the pancreas with larger gas cavities (white arrow); F: Gas confined to the tail of the pancreas with larger gas cavities (white arrow) and exudate involving the anterior fascia of the left kidney.