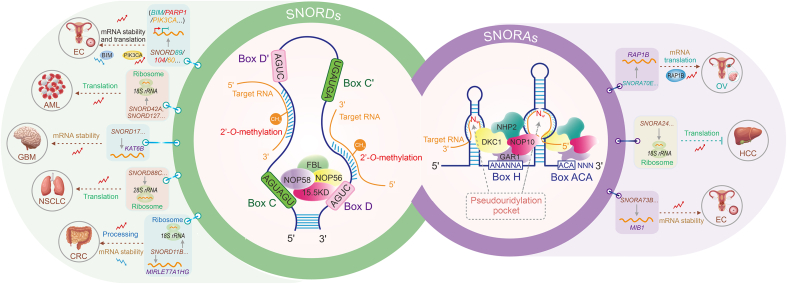
Fig. 1.
The classical mechanisms of small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs) involved in tumor initiation and development. Based on conserved sequence elements, snoRNAs are classified as C/D box snoRNAs (SNORDs) and H/ACA box snoRNAs (SNORAs). SNORDs contain sequence elements termed C (UGAUGA) and D (CUGA) boxes, usually present in duplicates (C' and D' boxes). SNORAs contain sequence elements termed H (ANANNA) and ACA boxes. SNORDs are responsible for the 2'-O-methylation modification of target RNAs by binding with proteins fibrillarin (FBL), nucleolar protein 56 (NOP56), NOP58, and 15.5KD. SNORAs are responsible for the pseudouridine modification of target RNAs by binding with proteins dyskerin pseudouridine synthase 1 (DKC1), GAR1 ribonucleoprotein (GAR1), NHP2 ribonucleoprotein (NHP2), and nucleolar protein 10 (NOP10). BIM: B cell lymphoma-2 (BCL-2)-like protein 11; PARP1: poly (adenosine diphosphate (ADP)-ribose) polymerase 1; PIK3CA: phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit alpha; mRNA: messenger RNA; EC: endometrial cancer; 18S rRNA: 18S ribosomal RNA; AML: acute myeloid leukemia; KAT6B: lysine acetyltransferase 6B; GBM: glioblastoma; NSCLC: non-small cell lung cancer; CRC: colorectal cancer; RAP1B: RAS-related protein 1B; OV: ovarian cancer; HCC: hepatocellular carcinoma; MIB1: mindbomb E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 1.