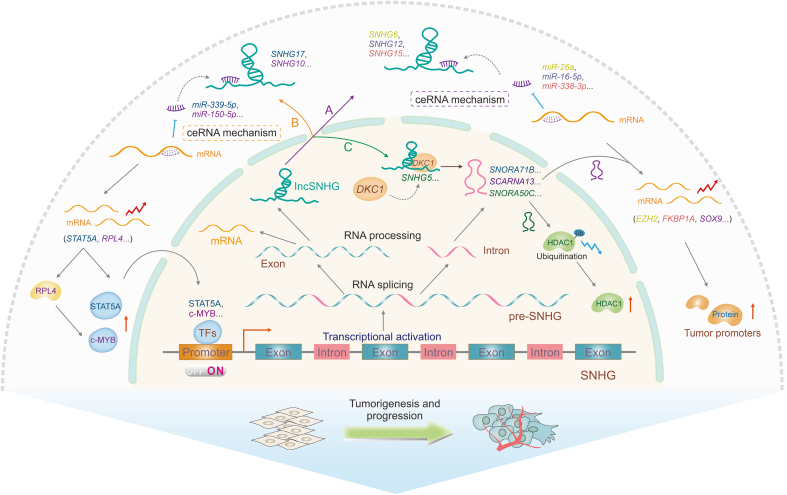
Fig. 4.
Regulatory mechanisms of small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs) derived from long non-coding snoRNA host gene (lncSNHGs) induce consistent biological functions in cancer. Long non-coding RNA snoRNA host genes (lncRNA SNHGs) and their homologous snoRNAs are derived from the same primary transcript, pre-SNHGs. SnoRNAs are usually derived from introns and lncRNA SNHGs are usually derived from exons. LncRNA SNHGs and snoRNAs participate in tumorigenesis and development through three regulatory pathways. (A) LncRNA SNHGs sponge microRNAs (miRNAs) through the ceRNA mechanism and inhibit the degradation of downstream messenger RNAs (mRNAs), which in turn promotes tumor progression. (B) LncRNA SNHGs, through the competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) mechanism, upregulate transcription factors, forming a positive feedback loop to upregulate their homologous snoRNAs. (C) LncRNA SNHG5 recruits dyskerin pseudouridine synthase 1 (DKC1) to promote SNORA50C accumulation and inhibits histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) ubiquitination, promoting hepatocellular cancer progression. The yellow color denotes SNHG6/miR-26a/enhancer of zeste 2 polycomb repressive complex 2 subunit (EZH2) axis. The grey color denotes SNHG12/miR-16-5p axis. The peach color denotes SNHG15/miR-338-3p/FK506-binding protein (FKBP) prolyl isomerase 1A (FKBP1A) axis. The blue color denotes SNHG17/miR-339-5p/signal transducer and activator of transcription 5A (STAT5A)/SNORA71B axis. The purple denotes SNHG10/miR-150-5p/ribosomal protein L4 (RPL4)/MYB proto-oncogene, transcription factor (c-Myb)/SCARNA13/SRY-box transcription factor 9 (SOX9) axis. The green denotes SNHG5/DKC1/SNORA50C/HDAC1 axis. TFs: transcription factors.