Abstract
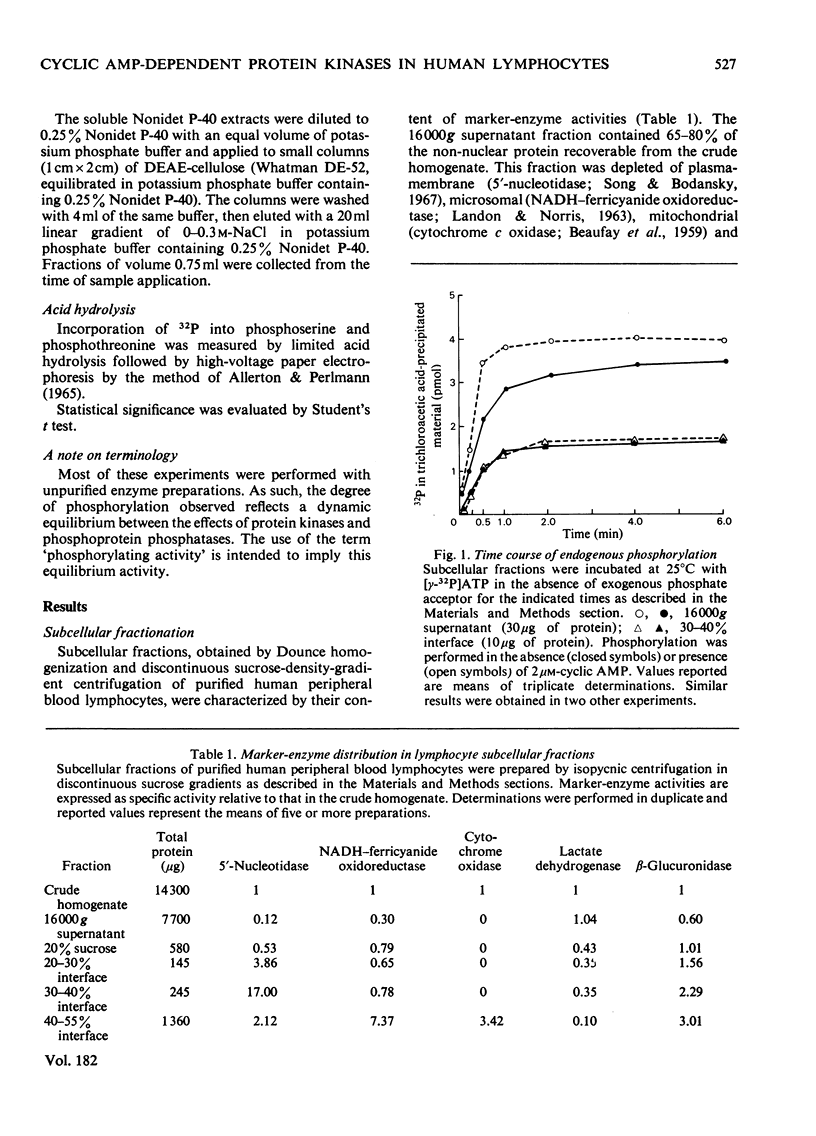
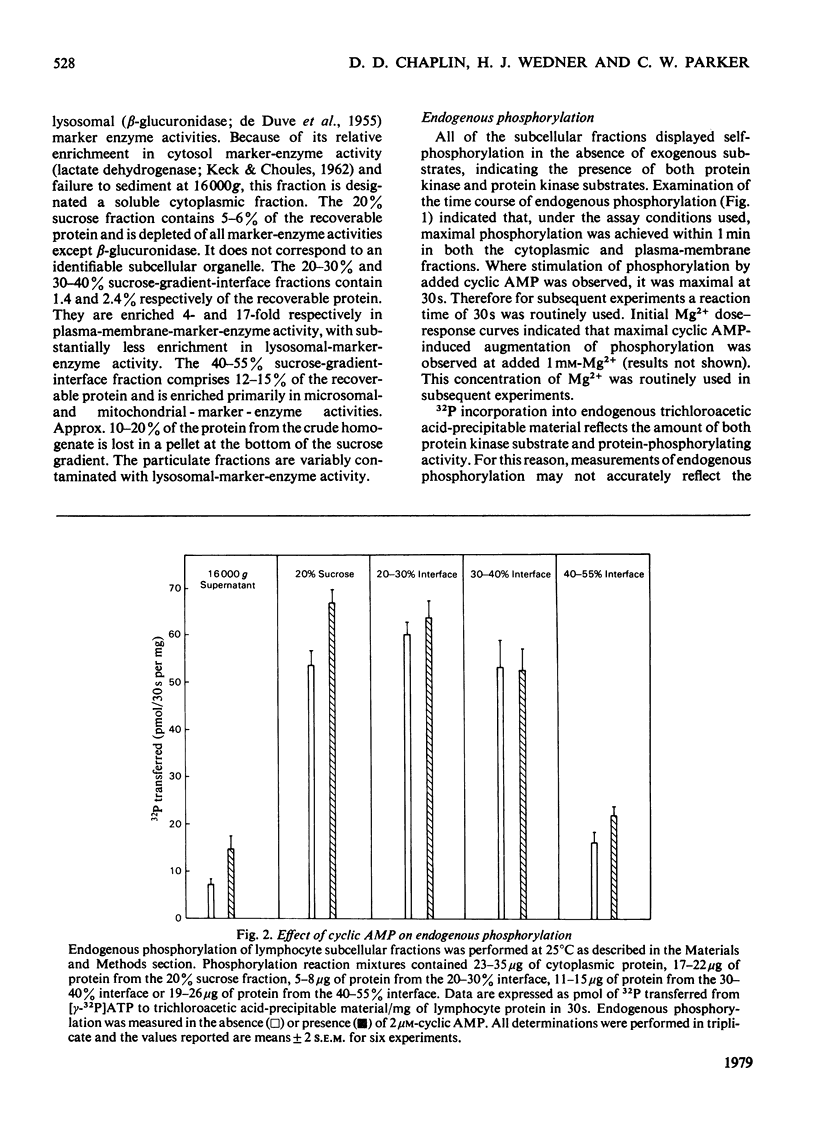
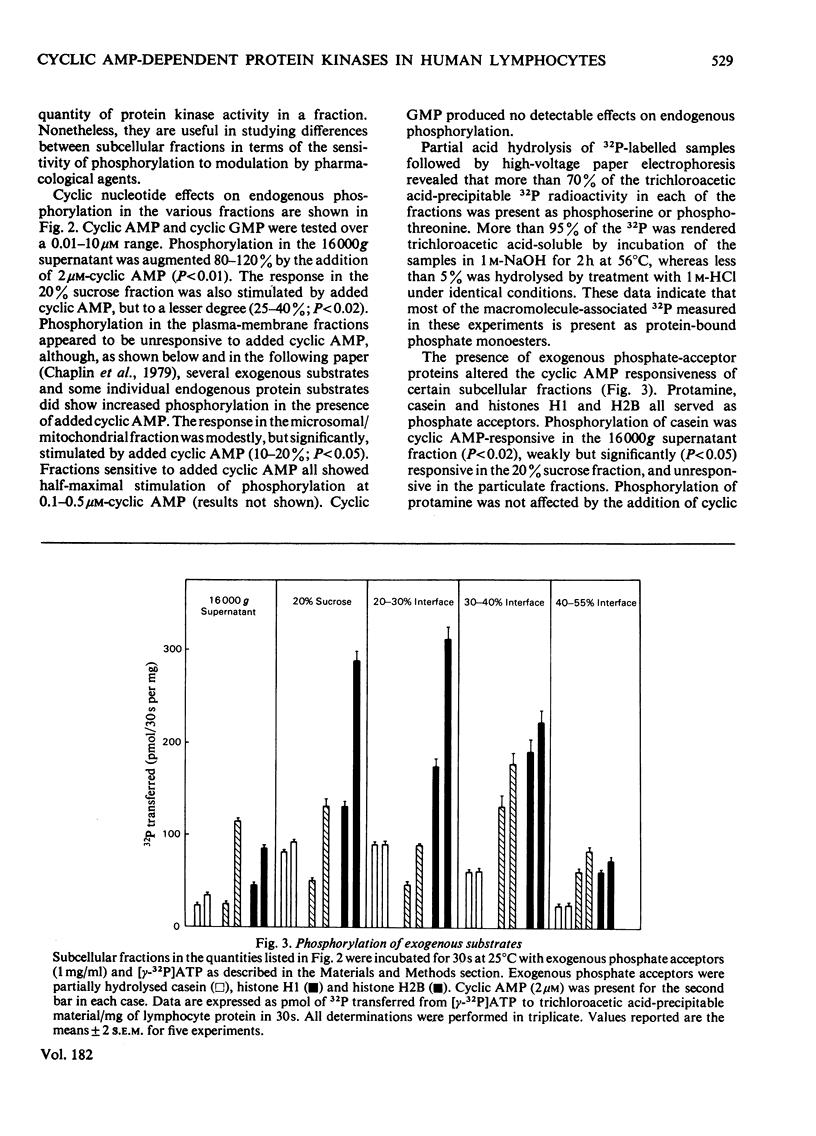
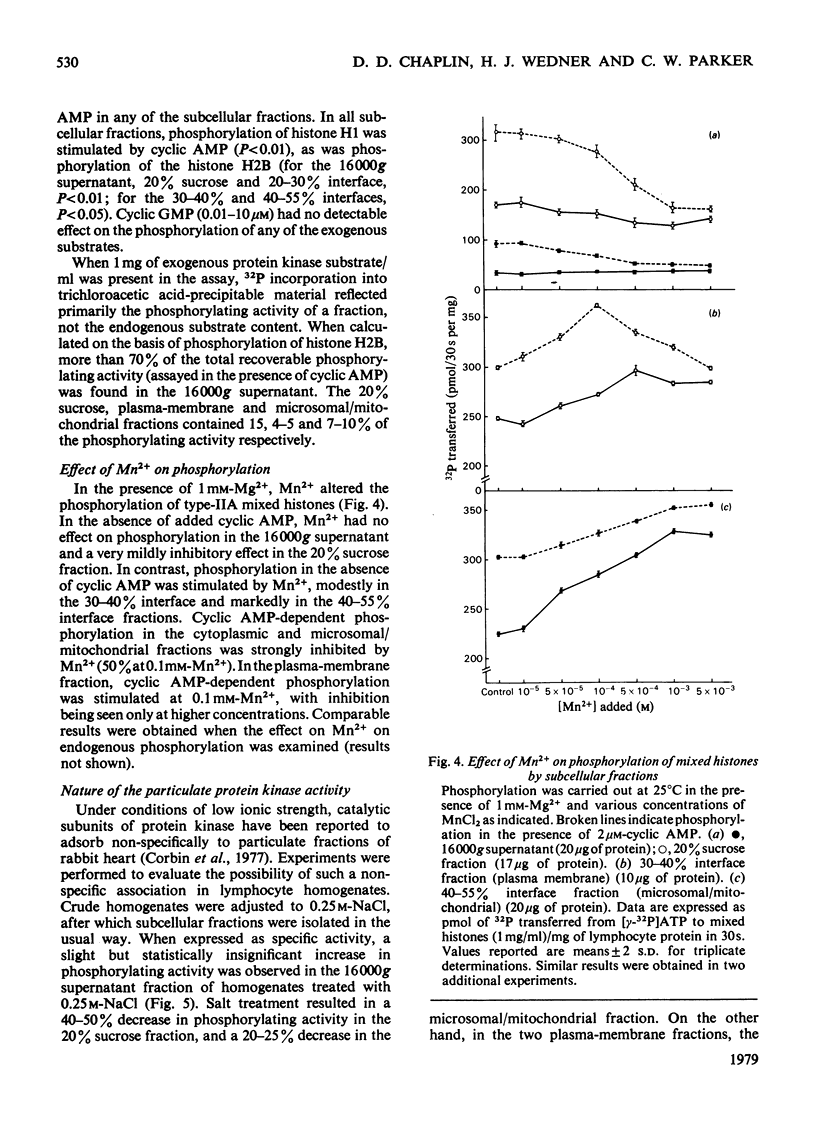
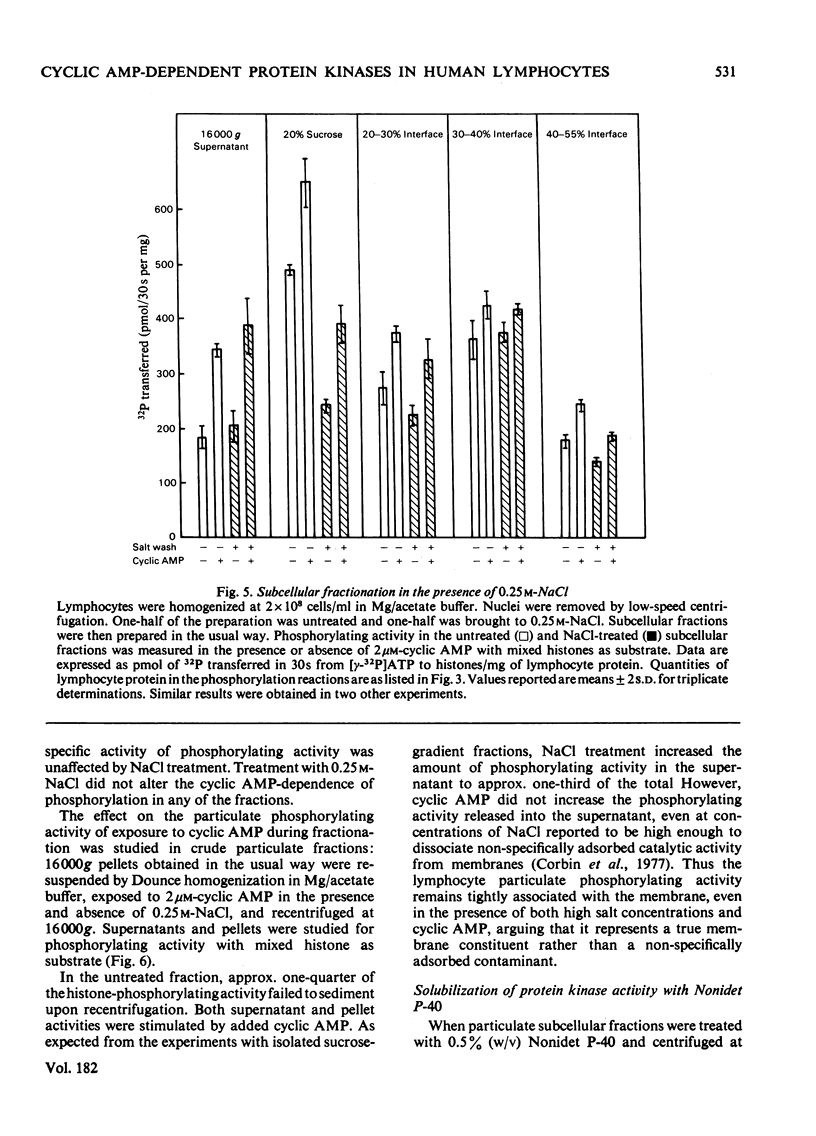
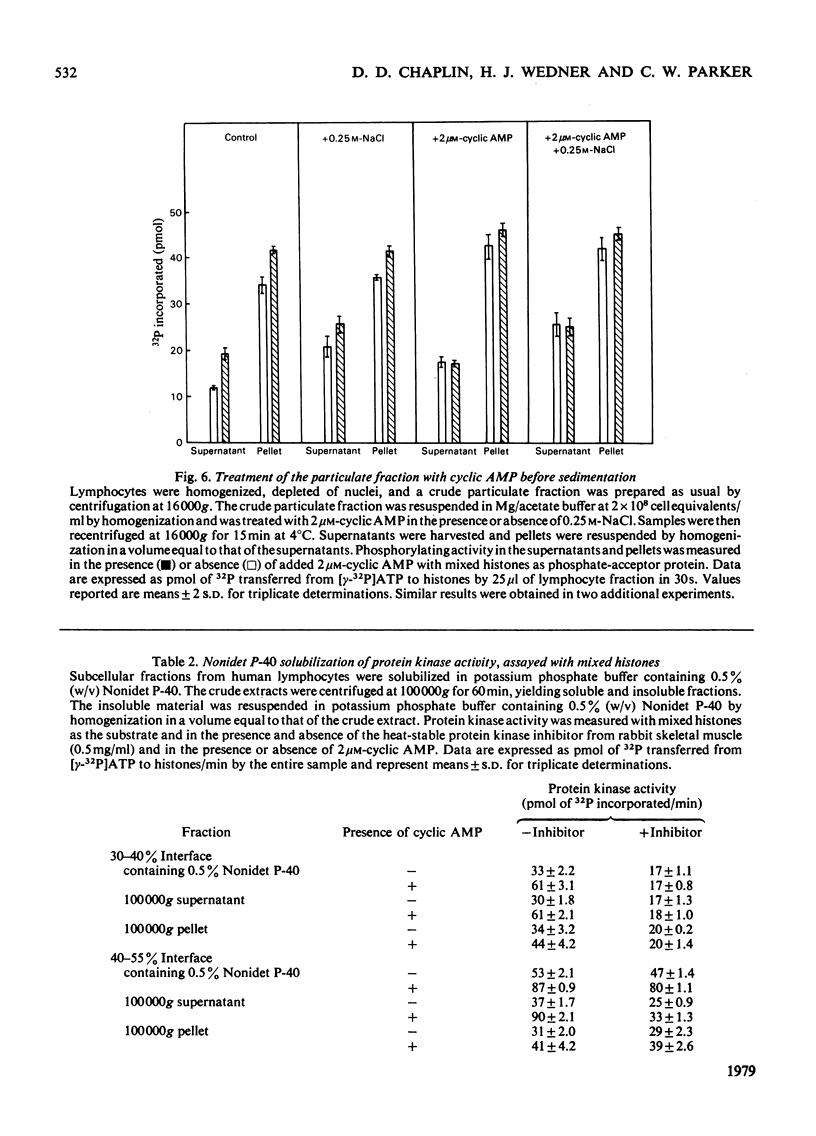
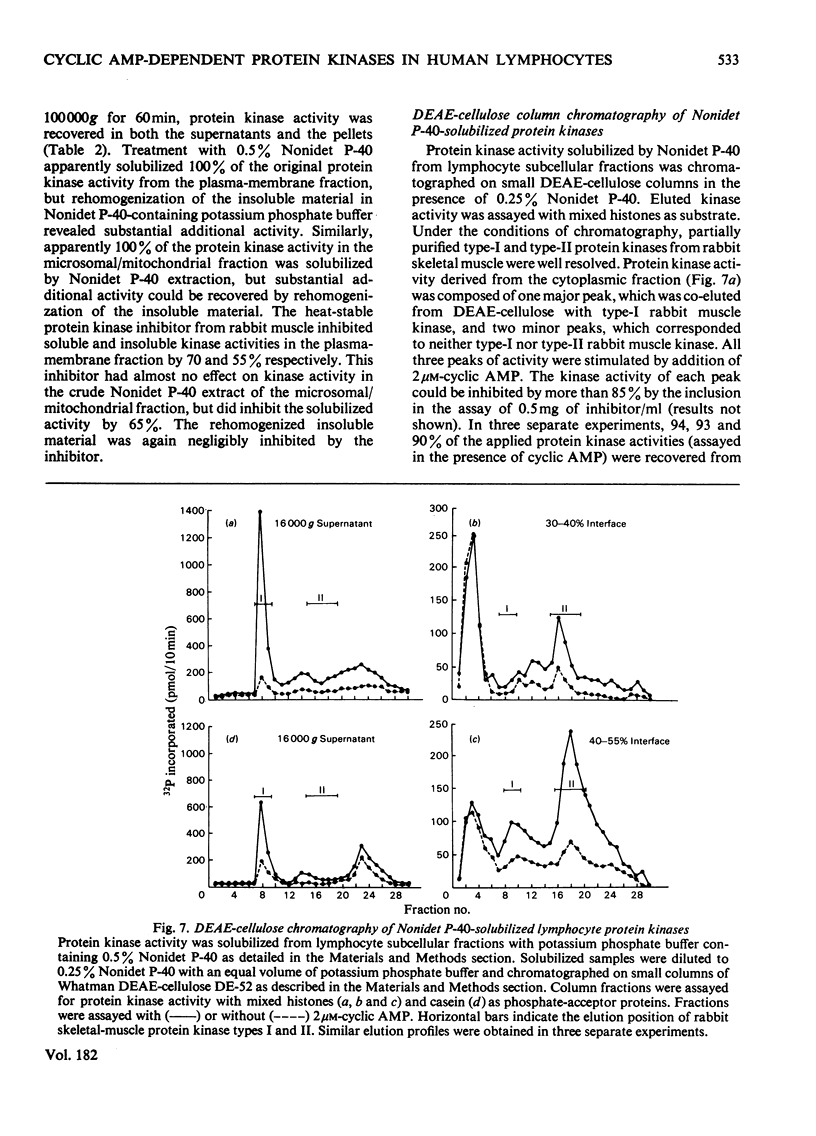
Cytoplasmic and membrane fractions prepared from human peripheral-blood lymphocytes both contained cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase activity and endogenous protein kinase substrates. Protein kinase activity in the particulate fractions was not eluted with 0.25 M-NaCl, suggesting that it was not derived from non-specifically absorbed soluble cytoplasmic protein kinase. Nor was the particulate protein kinase activity eluted by treatment with cyclic AMP, suggesting that the catalytic subunit is membrane-bound and arguing against cyclic AMP-induced translocation of particulate activity. Cyclic AMP-dependent protein-phosphorylating activity in the cytoplasmic fraction was highly sensitive to inhibition by Mn2+, and was co-eluted from DEAE-cellulose primarily with type-I rabbit skeletal-muscle kinase. Cyclic AMP-dependent phosphorylating activity in the plasma-membrane fractions was stimulated at low [Mn2+] and inhibited only at high [Mn2+]. When solubilized with Nonidet P-40, plasma-membrane protein kinase was co-eluted from DEAE-cellulose with type-II rabbit muscle kinase. These differences, together with the strong association of the particulate kinases with the particulate fraction, suggest the possibility of compartmentalized protein phosphorylation in intact lymphocytes.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allerton S. E., Perlmann G. E. Chemical characterization of the phosphoprotein phosvitin. J Biol Chem. 1965 Oct;240(10):3892–3898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEAUFAY H., BENDALL D. S., BAUDHUN P., WATTIAUX R., DE DUVE C. Tissue fractionation studies. 13. Analysis of mitochondrial fractions from rat liver by density-gradient centrifuging. Biochem J. 1959 Dec;73:628–637. doi: 10.1042/bj0730628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbier R., Colobert L. Identification dans le lymphocyte humain, de protéine-kinases modulées par l'AMP-3',5'-phosphodiester. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1975 Apr 7;280(13):1619–1622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brittinger G., Hirschhorn R., Douglas S. D., Weissmann G. Studies on lysosomes. XI. Characterization of a hydrolase-rich fraction from human lymphocytes. J Cell Biol. 1968 May;37(2):394–411. doi: 10.1083/jcb.37.2.394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byus C. V., Klimpel G. R., Lucas D. O., Russell D. H. Type I and type II cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase as opposite effectors of lymphocyte mitogenesis. Nature. 1977 Jul 7;268(5615):63–64. doi: 10.1038/268063a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaplin D. D., Wedner H. J., Parker C. W. Protein phosphorlyation in human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Phosphorylation of endogenous plasma membrane and cytoplasmic proteins. Biochem J. 1979 Aug 15;182(2):537–546. doi: 10.1042/bj1820537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin J. D., Sugden P. H., Lincoln T. M., Keely S. L. Compartmentalization of adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate and adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase in heart tissue. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 10;252(11):3854–3861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE DUVE C., PRESSMAN B. C., GIANETTO R., WATTIAUX R., APPELMANS F. Tissue fractionation studies. 6. Intracellular distribution patterns of enzymes in rat-liver tissue. Biochem J. 1955 Aug;60(4):604–617. doi: 10.1042/bj0600604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisen S. A., Wedner H. J., Parker C. W. Isolation of pure human peripheral blood T-lymphocytes using nylon wool columns. Immunol Commun. 1972;1(6):571–577. doi: 10.3109/08820137209022965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadden J. W., Hadden E. M., Haddox M. K., Goldberg N. D. Guanosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate: a possible intracellular mediator of mitogenic influences in lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Oct;69(10):3024–3027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.3024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jungmann R. A., Lee S., DeAngelo A. B. Translocation of cytoplasmic protein kinase and cyclic adenosine monophosphate-binding protein to intracellular acceptor sites. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1975;5:281–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KECK K., CHOULES E. A. The differential binding of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) isozymes to ribonucleoprotein particles. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1962 Nov;99:205–209. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(62)90001-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp B. E., Froscio M., Rogers A., Murray A. W. Multiple protein kinases from human lymphocytes. Identification enzymes phosphorylating exogenous histon and casein. Biochem J. 1975 Feb;145(2):241–249. doi: 10.1042/bj1450241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANDON E. J., NORRIS J. L. Sodium- and potassium-dependent adenosine triphosphatase activity in a rat-kidney endoplasmic reticulum fraction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 May 14;71:266–276. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91081-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto E., Petzold G. L., Harris J. S., Greengard P. Dissociation and concomitant activation of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase by histone. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jul 16;44(2):305–312. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90600-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Froscio M., Kemp B. E. Histone phosphatase and cyclic nucleotide-stimulated protein kinase from human lymphocytes. Biochem J. 1972 Oct;129(5):995–1002. doi: 10.1042/bj1290995a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. W., Sullivan T. J., Wedner H. J. Cyclic AMP and the immune response;. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1974;4(0):1–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piras M. M., Horenstein A., Piras R. Identification of multiple protein kinases in normal human lymphocytes. Enzyme. 1977;22(4):219–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. W., Steiner A. L., Newberry W. M., Jr, Parker C. W. Cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate in human lymphocytes. Alterations after phytohemagglutinin stimulation. J Clin Invest. 1971 Feb;50(2):432–441. doi: 10.1172/JCI106510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snider D. E., Jr, Parker C. W. Adenylate cyclase activity in lymphocyte subcellular fractions. Characterization of non-nuclear adenylate cyclase. Biochem J. 1977 Mar 15;162(3):473–482. doi: 10.1042/bj1620473a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song C. S., Bodansky O. Subcellular localization and properties of 5'-nucleotidase in the rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1967 Feb 25;242(4):694–699. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedner H. J., Parker C. W. Lymphocyte activation. Prog Allergy. 1976;20:195–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedner H. J., Parker C. W. Protein phosphorylation in human peripheral lymphocytes - stimulation by phytohemagglutinin and N6 monobutyryl cyclic AMP. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Feb 17;62(4):808–815. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90394-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


