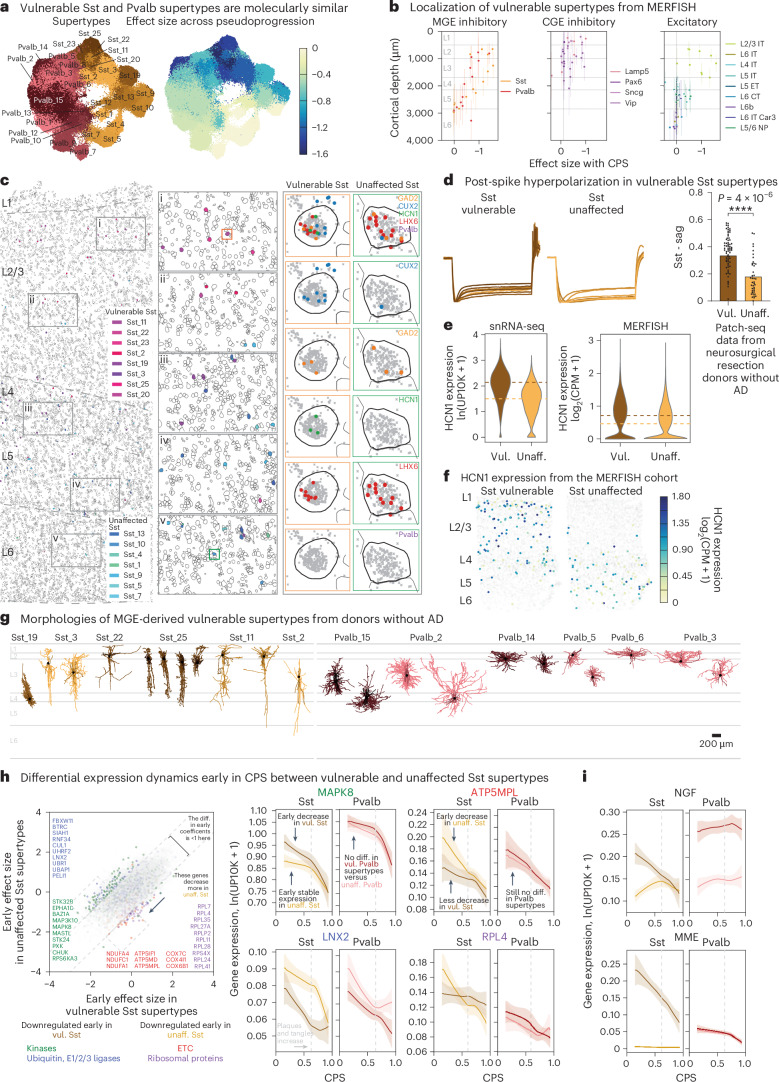
Fig. 5. Changes in superficial vulnerable MGE-derived inhibitory interneurons with common electrophysiological feature.
a, UMAP coordinates for MGE interneurons color-coded according to supertype (left) or the effect size of the relative changes in abundance from scCODA along the CPS (right). b, Scatter plots relating the effect size of the changes in abundance to the cortical depth for each neuronal supertype. Each point indicates the MERFISH-derived mean depth of the supertype; the error bars indicate the s.d. n represents the total number of MERFISH cells with quantified cortical depth (n = 349,941). c, Example MERFISH data from early CPS (0.23), with cell locations and boundaries. Cortical layers are separated by the dashed gray lines. Vulnerable Sst neurons are indicated by pink-purple hues; unaffected neurons are indicated by green-blue hues. d, Left, electrophysiological traces showing post-spike membrane potential hyperpolarization over time (y axis) in vulnerable Sst neurons recorded from human donors without AD. Right, bar and swarm plot indicating the Sag distributions. A logistic regression test was used to identify the differential electrophysiological features (P = 4 × 10−6). The P values for the differential intrinsic features are shown in Supplementary Table 8. n represents the total number of Sst cells profiled using patch-seq (n = 209). e, Violin plots of HCN1 expression in Sst neurons in snRNA-seq (left) and MERFISH (right). The colored dashed lines represent the mean expression. ln(UP10K + 1), natural log of UMIs/10,000 + 1. log2(counts per million (CPM) + 1). The statistical test was a negative binomial regression implemented in Nebula as described in the Methods. f, Scatter plot of Sst cells indicating cell position and HCN1 expression level in an early CPS donor (0.23). Superficial Sst cells have higher HCN1 expression. g, Patch-seq-derived morphological reconstructions of vulnerable MGE-derived interneurons from donors without AD. Dendrites are colored according to supertype. h, Scatter plot relating the mean early effect size for genes in vulnerable versus unaffected Sst supertypes. Gene families with decreased expression in vulnerable types are shown in blue (ubiquitin ligases, P = 0.036) and green (kinases, P = 8.92 × 10−11). Gene families with decreased expression in unaffected types are shown in red (ETC, P value near 0) and purple (ribosomal proteins, P value near 0). The statistical test is a negative binomial regression implemented in Nebula and gene family enrichment tests as described in the Methods and Supplementary Note. Right, LOESS regression plots of mean gene expression for vulnerable (dark orange) and unaffected (light orange) Sst types and vulnerable (dark red) and unaffected (light red) Pvalb types. The center lines are the mean from the LOESS fits; uncertainly, lines represent the s.e. from 1,000 LOESS fits with 80% of the data randomly selected in each iteration. ln(UP10K + 1), natural log UMIs/10,000 + 1. i, LOESS regression plots as in h. NGF and MME gene expression decreased in vulnerable Sst supertypes. Center lines and error bars as in h. The cohort demographics can be found in Supplementary Table 1. g, Scale bar, 200 μm. Diff., difference; unaff., unaffected; vul., vulnerable.