Abstract
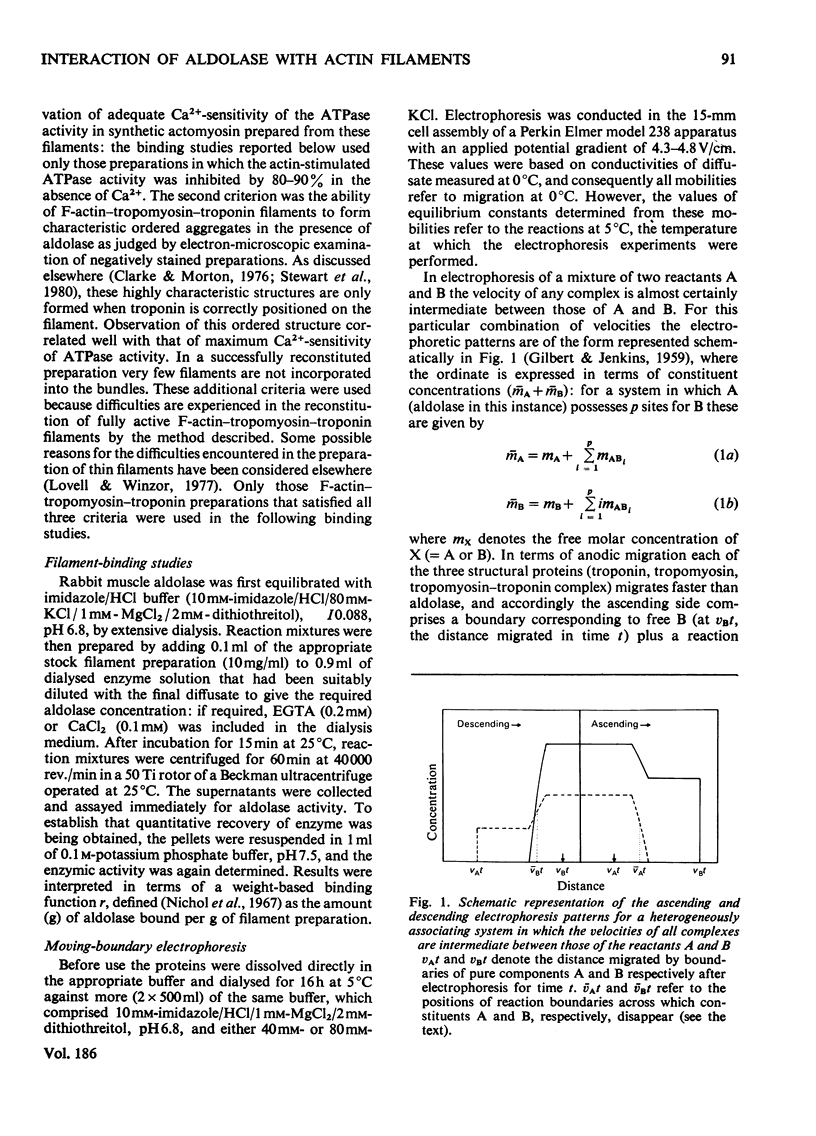
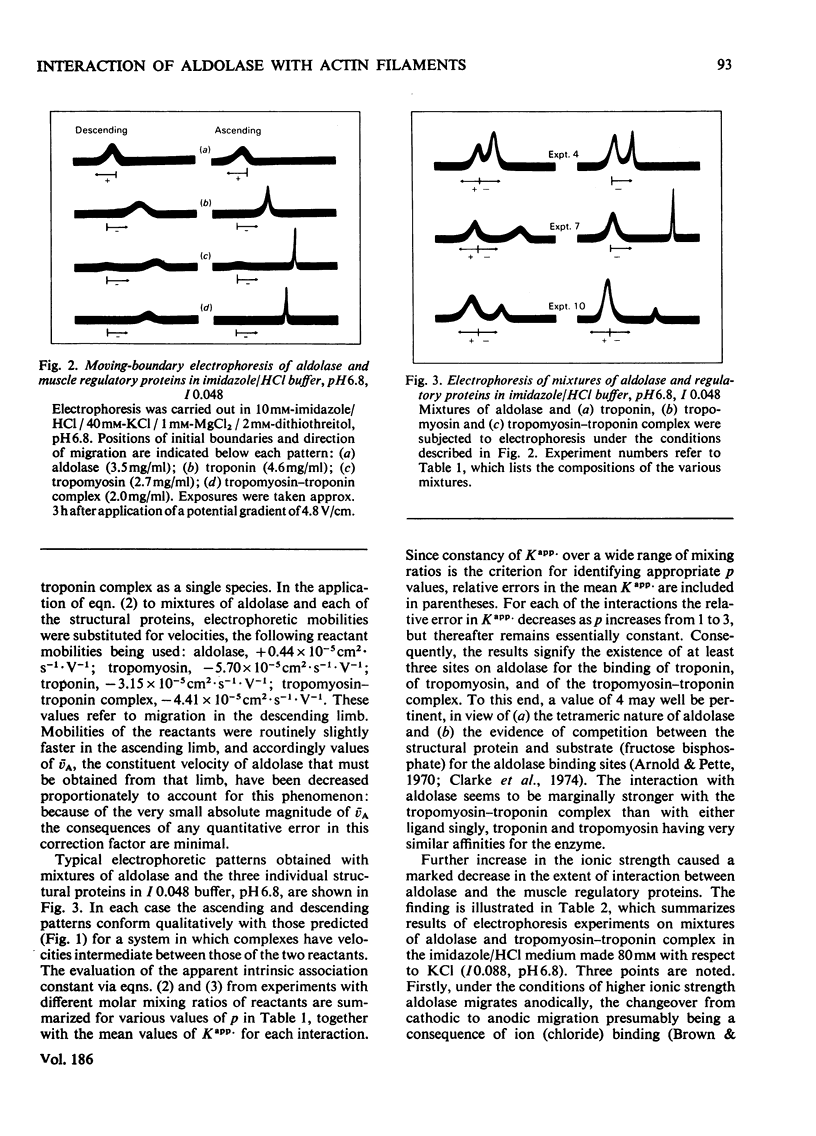
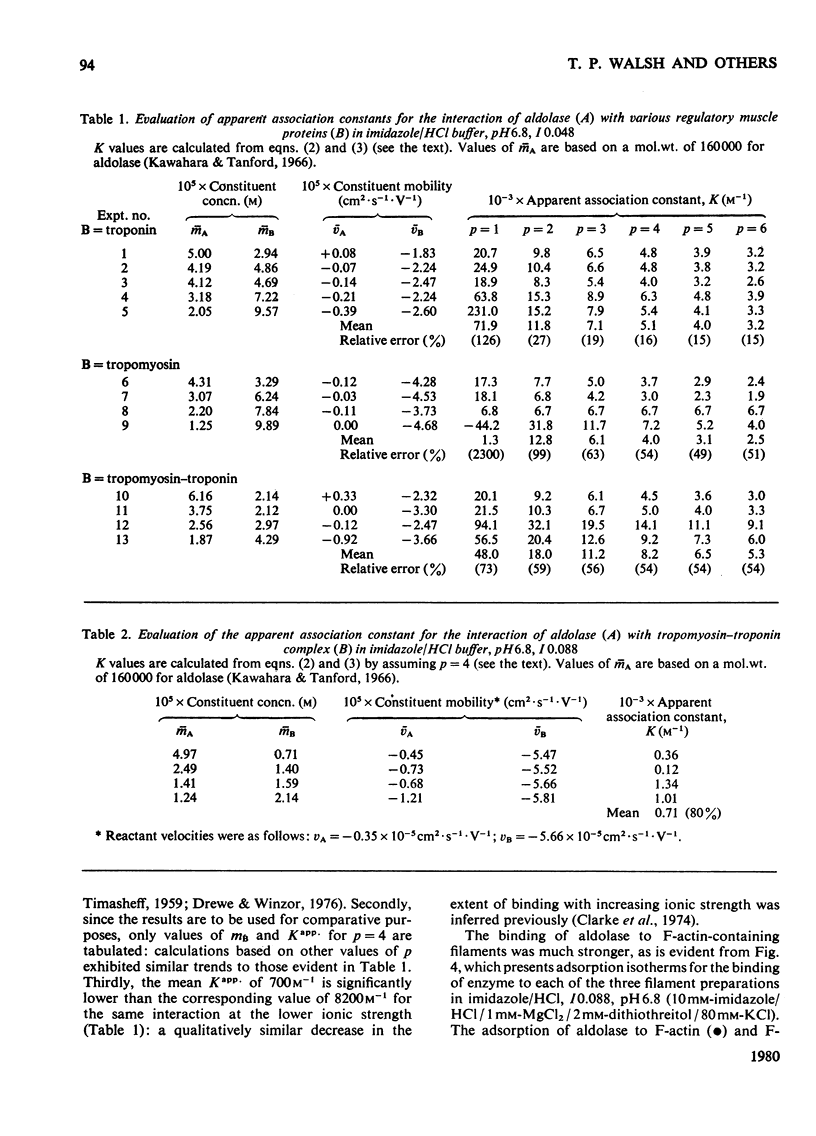
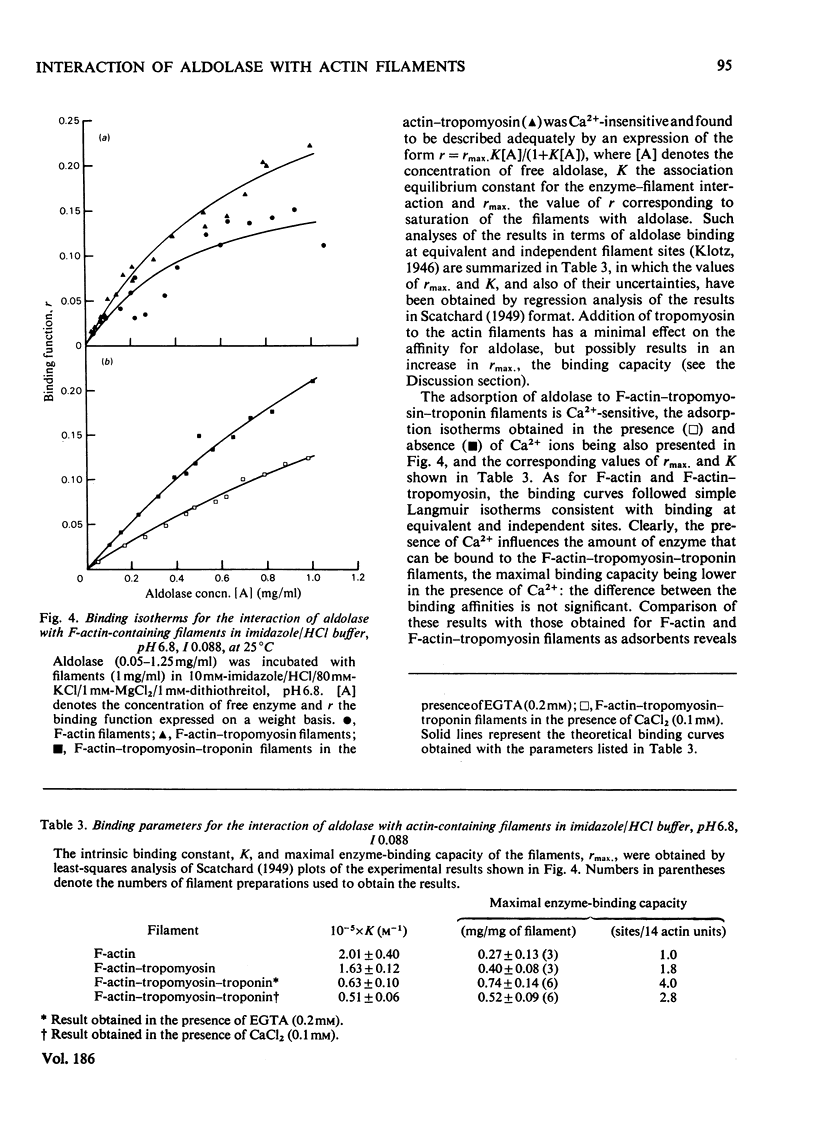
The interactions of aldolase with regulatory proteins of rabbit skeletal muscle were investigated by moving-boundary electrophoresis. A salt-dependent interaction of troponin, tropomyosin and the tropomyosin-troponin complex with aldolase was detected, the tropomyosin-troponin complex displaying a greater affinity for the enzyme than did either regulatory protein alone. The results indicate that aldolase possesses multiple binding sites (three or more) for these muscle proteins. Quantitative studies of the binding of aldolase to actin-containing filaments showed the interaction to be influenced markedly by the presence of these muscle regulatory proteins on the filaments. In imidazole/HCl buffer, I 0.088, pH 6.8, aldolase binds to F-actin with an affinity constant of 2 x 10(5) M-1 and a stoicheiometry of one tetrameric aldolase molecule per 14 monomeric actin units. Use of F-actin-tropomyosin as adsorbent results in a doubling of the stoicheiometry without significant change in the intrinsic association constant. With F-actin-tropomyosin-troponin a lower binding constant (6 x 10(4) M-1) but even greater stoicheiometry (4:14 actin units) are observed. The presence of Ca2+ (0.1 mM) decreases this stoicheiometry to 3:14 without affecting significantly the magnitude of the intrinsic binding constant.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnold H., Henning R., Pette D. Quantitative comparison of the binding of various glycolytic enzymes to F-actin and the interaction of aldolase with G-actin. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Sep 13;22(1):121–126. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01522.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold H., Pette D. Binding of aldolase and triosephosphate dehydrogenase to F-actin and modification of catalytic properties of aldolase. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Aug;15(2):360–366. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb01016.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold H., Pette D. Binding of glycolytic enzymes to structure proteins of the muscle. Eur J Biochem. 1968 Nov;6(2):163–171. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1968.tb00434.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briskey E. J., Fukazawa T. Myofibrillar proteins of skeletal muscle. Adv Food Res. 1971;19:279–360. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2628(08)60034-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CREETH J. M., NICHOL L. W. Evidence for the chemical interaction of urease in solution. Biochem J. 1960 Nov;77:230–239. doi: 10.1042/bj0770230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke F. M., Lovell S. J., Masters C. J., Winzor D. J. Beef muscle troponin: evidence for multiple forms of troponin-T. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 14;427(2):617–626. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(76)90205-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke F. M., Masters C. J. On the association of glycolytic components in skeletal muscle extracts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jul 17;358(1):193–207. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(74)90270-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke F. M., Masters C. J. On the association of glycolytic enzymes with structural proteins of skeletal muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jan 13;381(1):37–46. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(75)90187-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke F. M., Masters C. J., Winzor D. J. Interaction of aldolase with the troponin-tropomyosin complex of bovine muscle. Biochem J. 1974 Jun;139(3):785–788. doi: 10.1042/bj1390785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke F. M., Morton D. J. Aldolase binding to actin-containing filaments. Formation of paracrystals. Biochem J. 1976 Dec 1;159(3):797–798. doi: 10.1042/bj1590797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOTY P., EDSALL J. T. Light scattering in protein solutions. Adv Protein Chem. 1951;6:35–121. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60502-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drabikowski W., Rafalowska U., Dabrowska R., Szpacenko A., Barylko B. The effect of proteolytic enzymes on the troponin complex. FEBS Lett. 1971 Dec 15;19(3):259–263. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80528-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drewe R. H., Winzor D. J. An electrophoretic study of the reversible binding of phosphate to ovalbumin. Biochem J. 1976 Dec 1;159(3):737–741. doi: 10.1042/bj1590737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dölken G., Leisner E., Pette D. Immunofluorescent localization of glycogenolytic and glycolytic enzyme proteins and of malate dehydrogenase isozymes in cross-striated skeletal muscle and heart of the rabbit. Histochemistry. 1975;43(2):113–121. doi: 10.1007/BF00492440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiwata S. A study on the F-actin-tropomyosin-troponin complex. I. Gel-filament transformation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Mar 23;303(1):77–89. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(73)90150-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawahara K., Tanford C. The number of polypeptide chains in rabbit muscle aldolase. Biochemistry. 1966 May;5(5):1578–1584. doi: 10.1021/bi00869a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovell S. J., Winzor D. J. Self-association of troponin. Biochem J. 1977 Oct 1;167(1):131–136. doi: 10.1042/bj1670131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton D. J., Clarke F. M., Masters C. J. An electron microscope study of the interaction between fructose diphosphate aldolase and actin-containing filaments. J Cell Biol. 1977 Sep;74(3):1016–1023. doi: 10.1083/jcb.74.3.1016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichol L. W., Jackson W. J., Winzor D. J. A theoretical study of the binding of small molecules to a polymerizing protein system. A model for allosteric effects. Biochemistry. 1967 Aug;6(8):2449–2456. doi: 10.1021/bi00860a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearlstone J. R., Johnson P., Carpenter M. R., Smillie L. B. Primary structure of rabbit skeletal muscle troponin-T. Sequence determination of the NH2-terminal fragment CB3 and the complete sequence of troponin-T. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):983–989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearlstone J. R., Johnson P., Carpenter M. R., Smillie L. B. Primary structure of rabbit skeletal muscle troponin-T. Sequence determination of the NH2-terminal fragment CB3 and the complete sequence of troponin-T. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):983–989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penhoet E. E., Kochman M., Rutter W. J. Ioslation of fructose diphosphate aldolases A, B, and C. Biochemistry. 1969 Nov;8(11):4391–4395. doi: 10.1021/bi00839a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHARDS O. C., RUTTER W. J. Preparation and properties of yeast aldolase. J Biol Chem. 1961 Dec;236:3177–3184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigel P., Pette D. Intracellular localization of glycogenolytic and glycolytic enzymes in white and red rabbit skeletal muscle: a gel film method for coupled enzyme reactions in histochemistry. J Histochem Cytochem. 1969 Apr;17(4):225–237. doi: 10.1177/17.4.225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. A., Watt S. The regulation of rabbit skeletal muscle contraction. I. Biochemical studies of the interaction of the tropomyosin-troponin complex with actin and the proteolytic fragments of myosin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 10;246(15):4866–4871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart M., Morton D. J., Clarke F. M. Interaction of aldolase with actin-containing filaments. Structural studies. Biochem J. 1980 Jan 15;186(1):99–104. doi: 10.1042/bj1860099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh T. P., Clarke F. M., Masters C. J. Modification of the kinetic parameters of aldolase on binding to the actin-containing filaments of skeletal muscle. Biochem J. 1977 Jul 1;165(1):165–167. doi: 10.1042/bj1650165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson J. M., Grand R. J. The amino acid sequence of troponin I from rabbit skeletal muscle. Biochem J. 1975 Aug;149(2):493–496. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson J. M., Perry S. V., Cole H. A., Trayer I. P. The regulatory proteins of the myofibril. Separation and biological activity of the components of inhibitory-factor preparations. Biochem J. 1972 Mar;127(1):215–228. doi: 10.1042/bj1270215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods E. F. Molecular weight and subunit structure of tropomyosin B. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jun 25;242(12):2859–2871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


