Fig. 6.
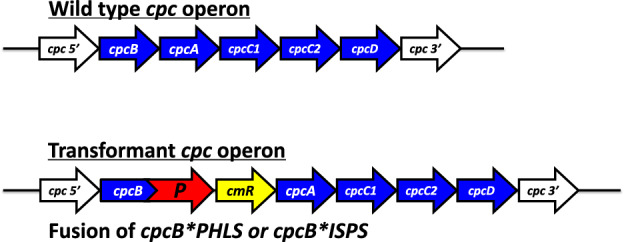
Schematic of DNA maps of the cpc operon in wild-type and Synechocystis fusion construct transformants. (Upper) The native cpc operon, as it occurs in wild-type Synechocystis, comprising the cpcB (phycocyanin β-subunit) and cpcA (phycocyanin α-subunit) DNA, as well as DNA encoding for the phycocyanin rod linker CpcC1, CpcC2, and CpcD proteins. This DNA operon configuration and sequence is referred to as the wild type (WT). (Lower). Replacement of the cpcB gene with fusion DNA construct cpcB*P, where P encodes for a protein of interest. The cpcB*P fusion construct is followed by DNA encoding the chloramphenicol (cmR) resistance cassette in an operon configuration. This transgenic DNA configuration enabled substantial accumulation of the recombinant CpcB*P fusion protein
