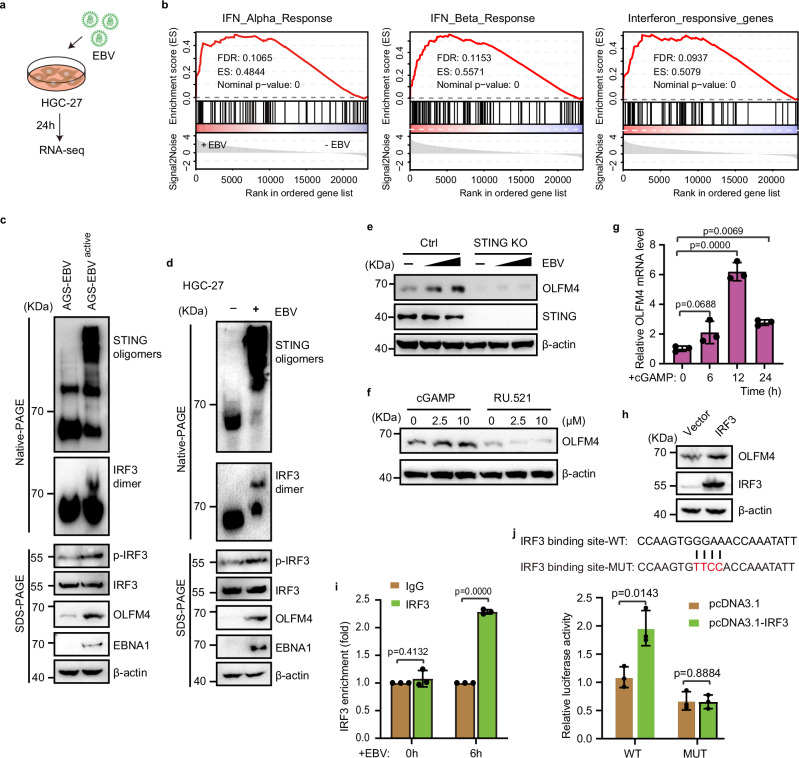
Fig. 3. EBV infection induced OLFM4 by cGAS-STING pathway.
a Workflow for transcriptome analysis of EBV infected HGC-27 cells. b GSEA analysis for the enrichment of IFNα, IFNβ and interferon responsive genes in 10 MOI EBV infected HGC-27 cells (n = 3 replicates/group). c Immunoblotting showing STING signaling pathway effector protein activity in AGS-EBV-infected HGC-27 cells. d Immunoblotting showing the indicated proteins in EBV-infected HGC-27 cells. e Immunoblotting showing OLFM4 expression in STING-knockout AGS cells after EBV treatment. Cells were treated with 0, 5, 10 MOI EBV for 48 h. f Immunoblotting showing OLFM4 expression in HGC-27 cells treated with STING agonist (cGAMP) or cGAS inhibitor (RU.521). Cells were treated with cGAMP or RU.521 for 24 h. g mRNA levels of OLFM4 in cGAMP (10 μM)-treated HGC-27 cells. h Immunoblotting showing OLFM4 expression in HGC-27 cells transfected with pcDNA3.1-IRF3 plasmid (n = 3 biological replicates/group). i CHIP-qPCR analysis of the IRF3 binding activity on the promoter region (−278 to −258) of OLFM4 (n = 3 biological replicates/group). HGC-27 cells were treated with 10 MOI EBV for 0, 6 h. j Dual-luciferase reporter assay to detect the relative activity of OLFM4 −278 to −258 promotor region (n = 3 biological replicates/group). All lanes are loaded with 50 μg of total protein (c–f, h). Representative of two independent experiments (c–j). Data are presented as mean ± s.d., analyzed for significant differences by performing two-tailed, one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post hoc analysis (g, i, j).