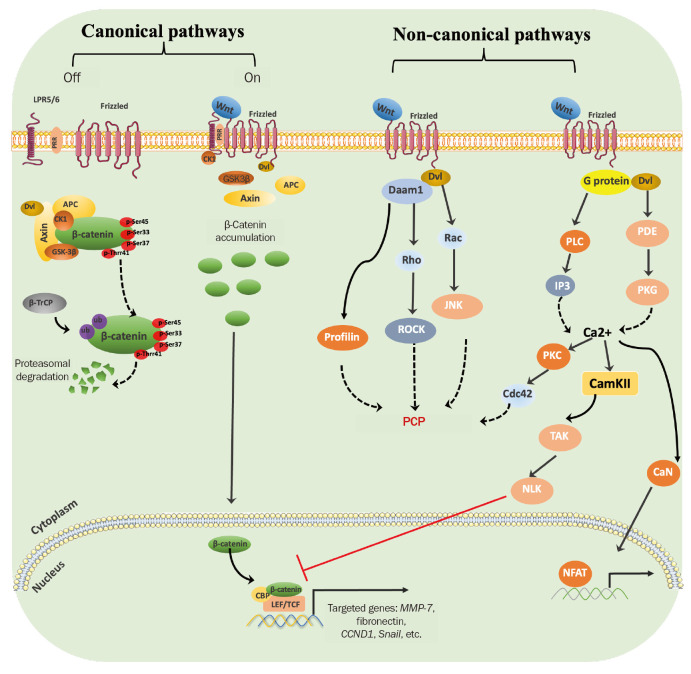
Figure 1. Wnt signaling pathway.
In the absence of Wnt ligands, the classical signaling pathway is off. At that time, β-catenin is phosphorylated at Ser45, Ser33, Ser37, and Thr41 by a destruction complex consisting of axin, GSK3β, Dvl, APC, and CK1. And then phosphorylated β-catenin is ubiquitylated by β-TrCP and degraded by the proteasome. When Wnt ligands are present and activated, they bind to coreceptors consisting of FZD protein and LRP5 or LRP6 on the cell surface, recruiting Dvl which induces dissociation of the destruction complex, and in turn results in intracellular accumulation of β-catenin. The accumulated β-catenin enters the nucleus and binds to TCF/LEF, thereby promoting target gene transcription. In the Wnt/PCP signaling pathway, Wnt ligands bind to frizzled receptors or their coreceptors (such as ROR-frizzled) which then recruit and activate Dvl proteins, which mediate Rho activation through Daam1. Activation of Rho in turn activates ROCK. Dvl also mediates Rac activation and then activates JNK. In addition, Daam1 can also mediate actin polymerization through the actin-binding protein Profilin. In the Wnt/Ca2+ pathway, Wnt ligands mediate G protein activation upon binding to frizzled receptors, which then recruit to activate Dvl, thereby activating the acid diesterase PDE. PKG can block the release of Ca2+, while PDE can increase the release of Ca2+ by inhibiting PKG. In addition, Dvl and G proteins can also activate PLC, which can activate IP3. The activation of IP3 induces the release of Ca2+ from the cell, thereby leading to an increase in Ca2+ levels. Ca2+ flux induced by these two pathways can activate second messengers such as PKC, CamKII, or CaN. Among them, CamKII activates TAK-NLK signaling and then antagonizes classical Wnt/β-catenin signaling through competing TCF. Activated CaN dephosphorylates NFAT, which then enters the nucleus and increases the transcription of its target genes. PKC can also engage in the Wnt/PCP pathway by activating the small GTPase Cdc42.
APC, adenomatous polyposis coli; β-TrCP, β-transducin repeat-containing protein; CamKII, calmodulin-dependent kinase II; CBP, cyclic adenosine monophosphate response-element binding protein; CK1, casein kinase 1; Daam1, dishevelled-associated activator of morphogenesis 1; Dvl, dishevelled; FZD, frizzled protein; GSK3β, glycogen synthase kinase 3β; IP, inositol triphosphate; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase; LEF, lymphoid enhancer binding factor; LRP, lipoprotein receptor protein; NFAT, nuclear factor of activated T-cells; NLK, nemo-like kinase; PCP, planar cell polarity; PDE, phosphodiesterase; PKC, protein kinase C; PKG, cGMP-dependent protein kinase; PLC, phospholipase C; Rac, Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate; ROCK, Rho-associated protein kinase; TAK, TGFβ-activated kinase; TCF, T-cell factor.