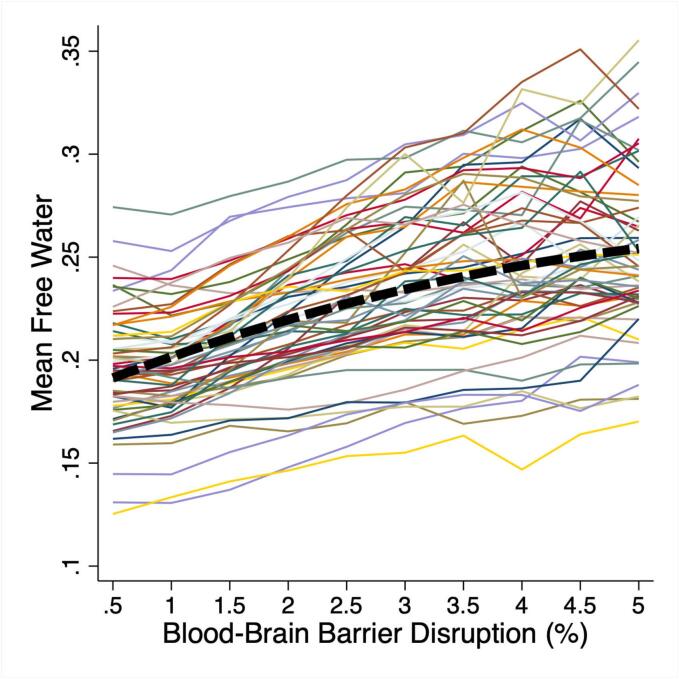
Fig. 3.
Elevated free water (FW) colocalizes with increased blood–brain barrier disruption (BBBD). White matter was divided into echelons by the degree of BBBD from 0 to 5 % (interval 0.5 %). Mean FW within each BBBD echelon was calculated and FW vs BBBD echelon was plotted for each participant. Mixed effects linear regression and a quadratic term for BBBD demonstrated that increasing BBBD was associated with increasing FW (p < 0.001).