Abstract
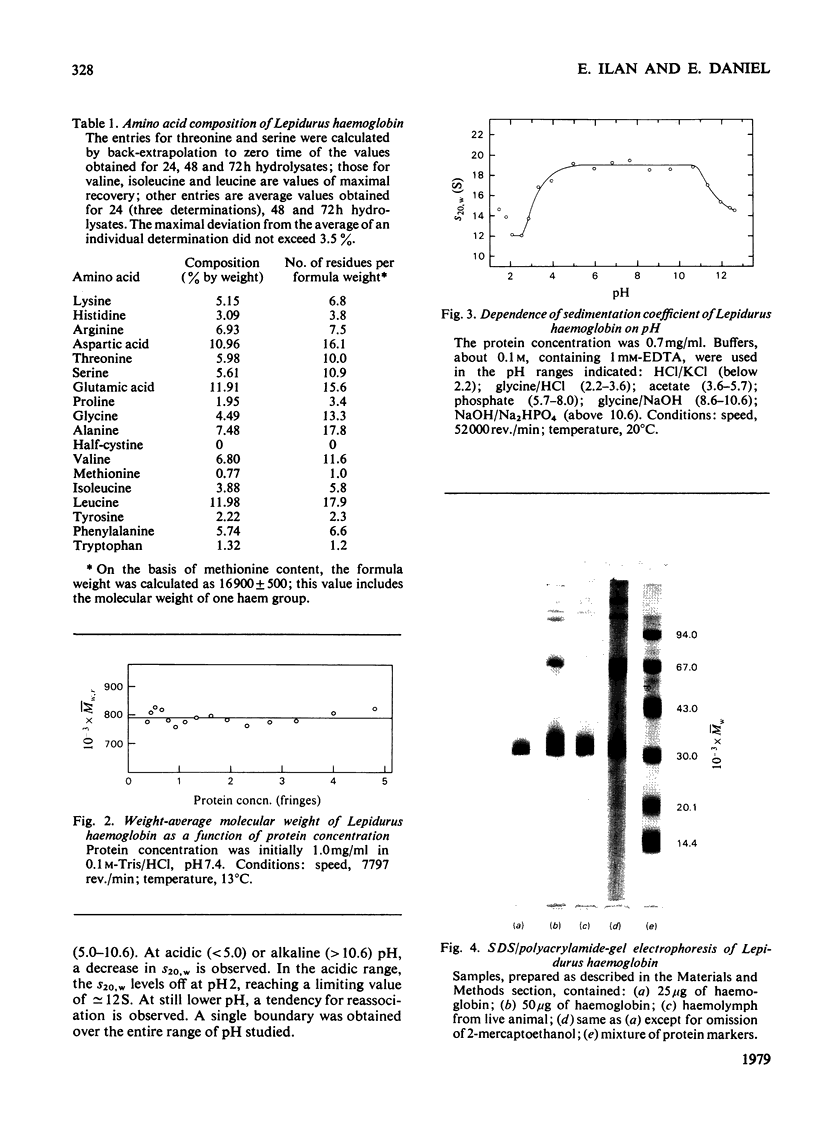
Haemoglobin from the tadpole shrimp, Lepidurus apus lubbocki, was found to have a sedimentation coefficient (s020,w) of 19.3 +/- 0.2 S and a molecular weight, as determined by sedimentation equilibrium, of 798000 +/- 20000. The amino acid composition showed the lack of cysteine and cystine residues. A haem content of 3.55 +/- 0.03% was determined, corresponding to a minimal mol.wt. of 17400 +/- 200. The pH-independence in the range pH 5-11 of the sedimentation coefficient indicates a relatively high stability of the native molecule. Sodium dodecyl sulphate/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis gave one band with mobility corresponding to a mol.wt. of 34000 +/- 1500. The molecular weight of the polypeptide chain was determined to be 32800 +/- 800 by sedimentation equilibrium in 6 M-guanidinium chloride and 0.1 M-2-mercaptoethanol. The findings indicate that Lepidurus haemoglobin is composed of 24 identical polypeptide chains, carrying two haem groups each.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antonini E., Chiancone E. Assembly of multisubunit respiratory proteins. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1977;6:239–271. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.06.060177.001323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ar A., Schejter A. Isolation and properties of the hemoglobin of the clam shrimp Cyzicus cf. hierosolymitanus (S. Fischer). Comp Biochem Physiol. 1970 Apr 1;33(3):481–490. doi: 10.1016/0010-406x(70)90365-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behlke J., Pfeil W., Blanck J., Ristau O., Rein H., Müller K., Mohr P., Scheler W. Molekulare und komplexchemische Studien am Methämoglobin von Chironomus thummi thummi sowie einiger isolierter Fraktionen. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1975;34(3):365–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behlke J., Scheler W. The molecular properties of the methaemoglobin of Chironomus plumosus L. in solution. Eur J Biochem. 1967 Dec;3(2):153–157. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1967.tb19510.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen S. T., Moise H. W., Waring G., Poon M. C. The hemoglobins of Artemia salina--III. Characterization. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1976;55(1):99–103. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(76)90180-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CASASSA E. F., EISENBERG H. THERMODYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF MULTICOMPONENT SOLUTIONS. Adv Protein Chem. 1964;19:287–395. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60191-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David M. M., Schejter A., Daniel E., Ar A., Ben-Shaul Y. Subunit structure of hemoglobin from the clam shrimp Cyzicus. J Mol Biol. 1977 Apr;111(2):211–214. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80125-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRS C. H. The oxidation of ribonuclease with performic acid. J Biol Chem. 1956 Apr;219(2):611–621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber R., Formanek H., Epp O. Kristallstrukturanalyse des Met-Erythrocruorins bei 5,5 Angstrom Auflösung. Naturwissenschaften. 1968 Feb;55(2):75–77. doi: 10.1007/BF00599482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinschmidt T., Braunitzer G. Die Sequenz eines dimeren Hämoglobins (Komponente IIbeta, Chironomus thummi thummi, Dipetera) Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1976 Dec;357(12):1805–1808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. C., Timasheff S. N. Partial specific volumes and interactions with solvent components of proteins in guanidine hydrochloride. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 15;13(2):257–265. doi: 10.1021/bi00699a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara H., Sasaki R. M. High recovery of tryptophan from acid hydrolysates of proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Apr 29;35(2):175–181. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90263-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moens L., Kondo M. Characterization of the extracellular haemoglobins of Artemia salina. Biochem J. 1977 Jul 1;165(1):111–119. doi: 10.1042/bj1650111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quitter S., Watts L. A., Crosby C., Roxby R. Molecular weights of aggregation states of Busycon hemocyanin. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jan 25;253(2):525–530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisler E., Eisenberg H. Interpretation of equilibrium sedimentation measurements of proteins in guanidine hydrochloride solutions. Partial volumes, density increments, and the molecular weight of the subunits of rabbit muscle aldolase. Biochemistry. 1969 Nov;8(11):4572–4578. doi: 10.1021/bi00839a051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugano H., Hoshi T. Purification and properties of blood hemoglobin from the fresh-water cladocera, Moina macrocopa and Daphnia magna. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Feb 16;229(2):349–358. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90194-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson P., Bleecker W., English D. S. Molecular size and subunit structure of the hemoglobins of Chironomus tentans. J Biol Chem. 1968 Sep 10;243(17):4463–4467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Pringle J. R., Osborn M. Measurement of molecular weights by electrophoresis on SDS-acrylamide gel. Methods Enzymol. 1972;26:3–27. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(72)26003-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YPHANTIS D. A. EQUILIBRIUM ULTRACENTRIFUGATION OF DILUTE SOLUTIONS. Biochemistry. 1964 Mar;3:297–317. doi: 10.1021/bi00891a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]