Fig. 2.
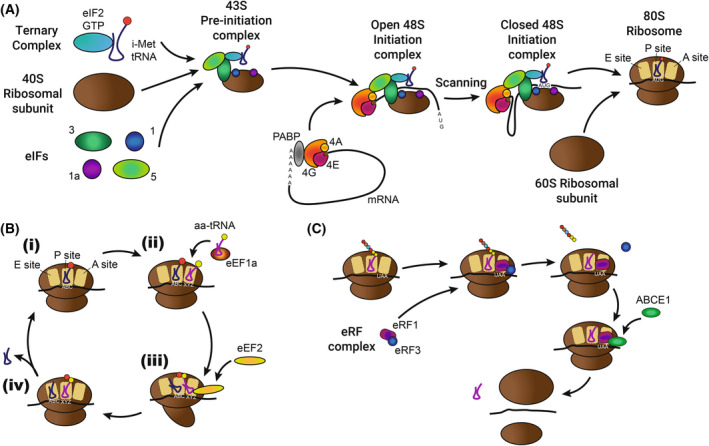
Canonical mechanism of translation. (A) Translation Initiation. The ternary complex, 40S ribosomal subunit and eIF3, eIF5, eIF1, eIF1a form the 43S pre‐initiation complex (PIC). The eIF4F complex, composed of eIF4A, eIF4G and eIF4E, binds the mRNA cap and poly‐A binding protein (PABP) to circularize the mRNA. The 43S PIC binds the eIF4F complex and scans along the mRNA until the initiator methionine (i‐met) tRNA of the ternary complex recognizes an AUG codon. The 60S ribosomal subunit is then recruited to form the 80S ribosome with the i‐met tRNA in the peptidyl transferase (P)‐site. (B) Translation elongation. (i) Following initiation or a round of translation, a ribosome has one tRNA in the P‐site. (ii) A codon‐matched amino‐acylated (aa‐)tRNA is recruited to the acceptor (A)‐site by eEF1a. (iii–iv) mRNA translocation occurs, mediated by eEF2, moving the tRNAs from the P‐ to the Exit (E)‐site, and A‐ to P‐site, adding one amino acid to the peptide chain. The E‐site tRNA is released and the process repeats from (i) until a stop codon is reached. (C) Translation termination. Once a stop codon is reached, it is recognized by the eRF1/3 complex, which causes the peptide chain to be released. The ribosome is then split for recycling.
