Fig. 4.
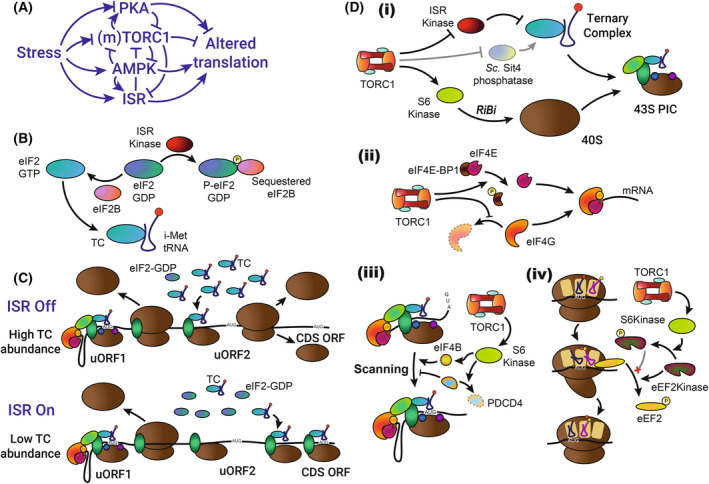
Changes to translation upon stress. (A) Stress impacts signalling from various kinases to alter translation. Arrowheads indicate activation, while barred lines indicate inhibition. ISR is the integrated stress response. (B) Inhibition of ternary complex formation by the ISR. ISR kinases phosphorylate eIF2α to sequester the eIF2 GEF and eIF2B, preventing GDP to GTP transition and re‐binding of initiator tRNA. (C) Regulation of ATF4/GCN4 translation by upstream open reading frames (ORFs) is dependent on ISR signalling. Following initiation and termination from uORF1, the restriction of ternary complex (TC) availability under conditions of ISR activation prevents premature re‐initiation at uORF2. This allows translation initiation from the start codon of the coding sequence (CDS) ORF. In mouse ATF4 mRNA, uORF2 overlaps the CDS ORF. For GCN4 mRNA, the uORF1 represented here is analogous to the first ORF pair (uORFs1&2) while uORF2 is analogous to the second ORF pair (uORFs3&4). (D) Impacts of the stress‐inhibited kinase TORC1 signalling on translation. (i) TORC1 inhibition restricts 43S pre‐initiation complex formation through ISR activation (see Fig. 4B) and reduced ribosome biogenesis (RiBi) through decreased S6Kinase activation. In S. cerevisiae, the TORC1‐inhibited phosphatase Sit4 can counter the ISR kinases. (ii) TORC1 inhibition restricts availability of the eIF4F components eIF4G (via increased degradation) and eIF4E (through eIF4E‐BP1 sequestration). (iii) TORC1 inhibition, and reduced S6Kinase activation, decreases eIF4B activation of eIF4A and prevents degradation of the eIF4A inhibitor PDCD4. (iv) Inhibition of TORC1, and resulting S6Kinase inhibition, allows eEF2Kinase to inhibit the ability of eEF2 in mRNA translocation.
