Figure 4.
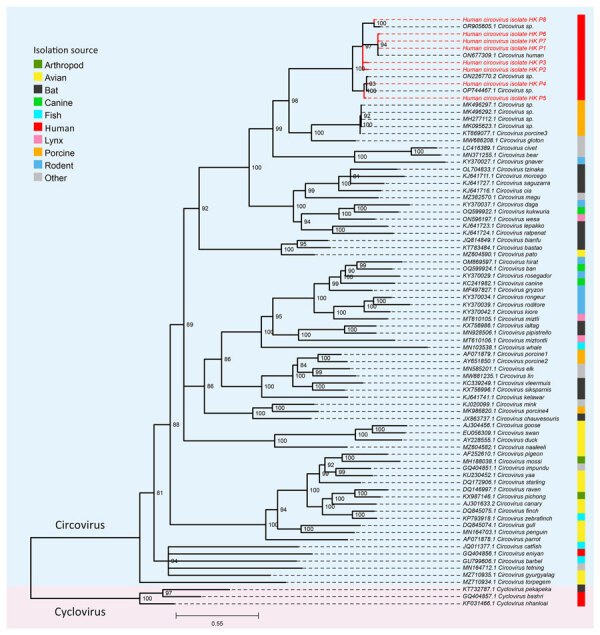
Phylogenetic tree of representative circoviruses and human circoviruses from study of human circovirus in patients with hepatitis, Hong Kong. Maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree was inferred from a multiple sequence alignment of complete representative Circovirus genomes and a mixture of full-length and partial genome sequences from this study (red text) using IQ-TREE (16). Three representative species of Cyclovirus were used as an outgroup for rooting the tree. Branch supports were assessed using the Shimodaira-Hasegawa–like approximate likelihood ratio test with 10,000 bootstrap replicates. Branches with <80% support were collapsed. Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site.
