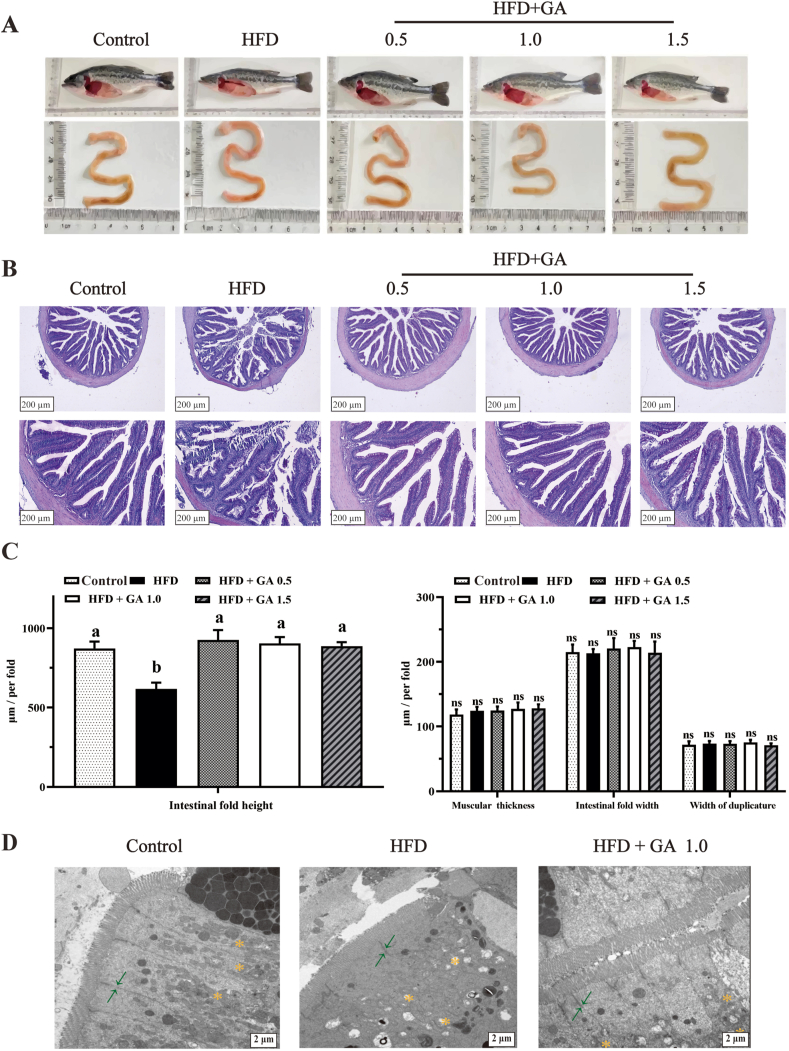
Fig. 1.
Glycyrrhetinic acid (GA) alleviates intestinal injury in largemouth bass induced by a high-fat diet (HFD). (A) The pictures of fish body and intestine. (B) Intestine histopathological analysis of largemouth bass. (C) The statistical analysis was performed on the intestinal fold height, intestinal fold width, muscular thickness, and width of duplicature. (D) Transmission electron microscope images of intestines of largemouth bass. The green arrows indicate the intestinal tight junction, and the orange star indicates mitochondrial damage (scale bar = 2 μm). The results are presented as mean ± SE of six replicates. Mean values with different letters indicate significant differences (P < 0.05), whereas those with the same letter or no letter indicate no significant differences. ns = no significant differences.