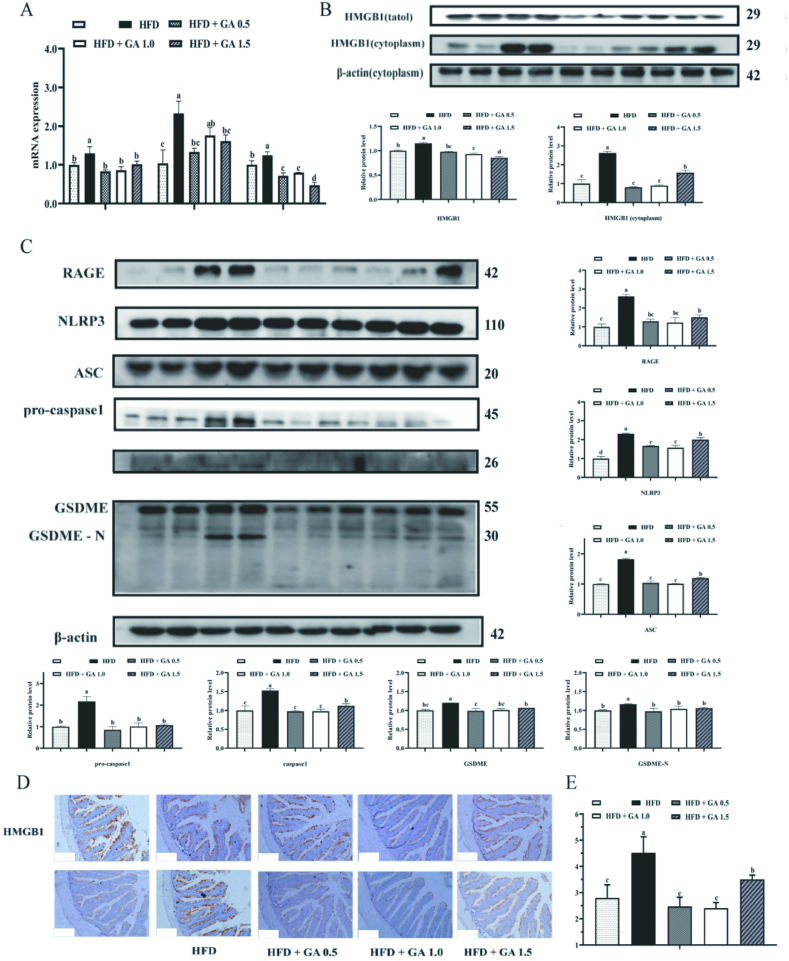
Fig. 4.
Effects of glycyrrhetinic acid (GA) on intestinal pyroptosis-related genes expression induced by high fat diets (HFD). (A) The mRNA expression of intestinal pyroptosis-related genes including cysteinyl aspartate specific proteinase 1 (caspase-1), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), interleukin-18 (IL-18). (B) Protein levels of total HMGB1 and cytoplasm HMGB1. HMGB1 = high mobility group box1. (C) Related protein levels of intestinal pyroptosis-related genes, including RAGE, NLRP3, ASC, pro-caspase-1, caspase-1, GSDME, GSDME-N. RAGE = receptor for advanced glycation end products; NLRP3 = NOD-like receptor family and pyrin domain contain 3; ASC = apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a C-terminal caspase recruitment domain; caspase-1 = cysteinyl aspartate specific proteinase 1; GSDME = gasdermin E; GSDME-N N-terminal domain of GSDME. (D) Immunohistochemistry for caspase-1 observed under a fluorescence microscope (scale bar = 100 μm). (E) Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) content in the serum. Bars with different letters indicate a significant difference (P < 0.05).