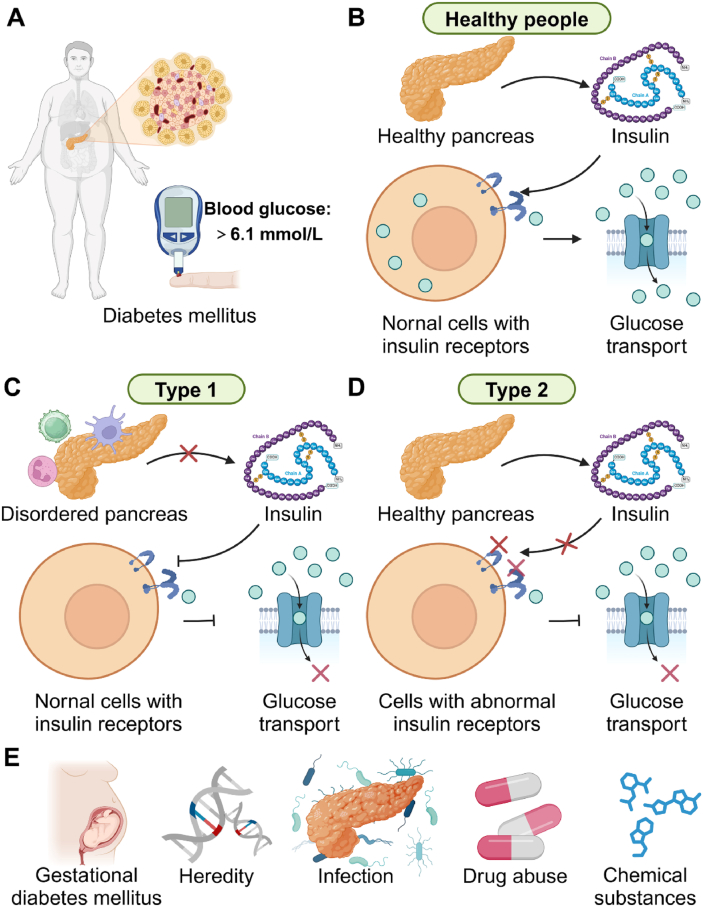
Fig. 1.
Types and occurrence mechanism of diabetes mellitus. (A) The fasting blood glucose concentration is more than 6.1 mmol/L, which may be diagnosed as diabetes mellitus. (B) For health people, the insulin is normally secreted, regularly interfacing with the receptors, finally completing blood glucose transport. (C) Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the body's immune system attacks and destroys insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas, leading to insulin deficiency. (D) Type 2 diabetes is a progressive condition where the body becomes resistant to the effects of insulin or doesn't produce enough insulin to maintain normal glucose levels. (E) For some idiopathic and secondary diabetes mellitus, the pregnancy, heredity, infection, drug abuse, and chemical substances would be considered as etiological factors.