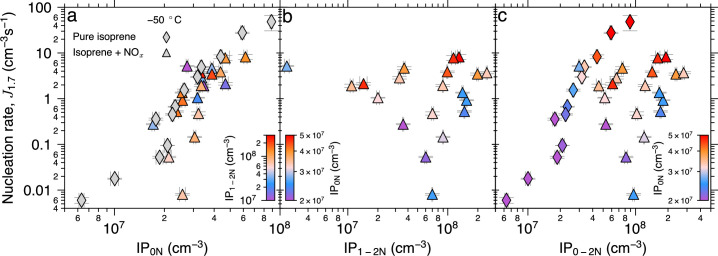
Extended Data Fig. 5. Particle-nucleation rates from IP-OOM at −50 °C, in the absence of acids.
Nucleation rates at 1.7 nm, J1.7, versus IP-OOM without nitrogen, IP0N (a), with nitrogen, IP1N + IP2N (b) and the sum, IP0-2N (c). Panel a indicates a mild enhancement of the nucleation rates with increased IP1N + IP2N. Panels b and c confirm that the nucleation rates are only weakly dependent on IP1N + IP2N. These data show that non-nitrate IP-OOM are primarily responsible for particle nucleation, with a smaller contribution from nitrate-containing isoprene products. The experimental conditions are: isoprene = 0.04–0.50 ppbv (0.14–1.7 × 1010 cm−3), O3 = 1.2–590 ppbv (4 × 1010 to 1.8 × 1013 cm−3), OH = 0.14–6.40 × 107 cm−3, HO2 = 1.6–17.0 × 108 cm−3, HO2/OH ratio = 11–118, NO = 0–0.18 ppbv, NO2 = 0–0.74 ppbv, RH = 29–61% and temperature = −50 °C. All experiments are carried out under galactic cosmic ray ionization (ambient-boundary-layer conditions). The error bars represent the standard deviation of the measurement at steady state.