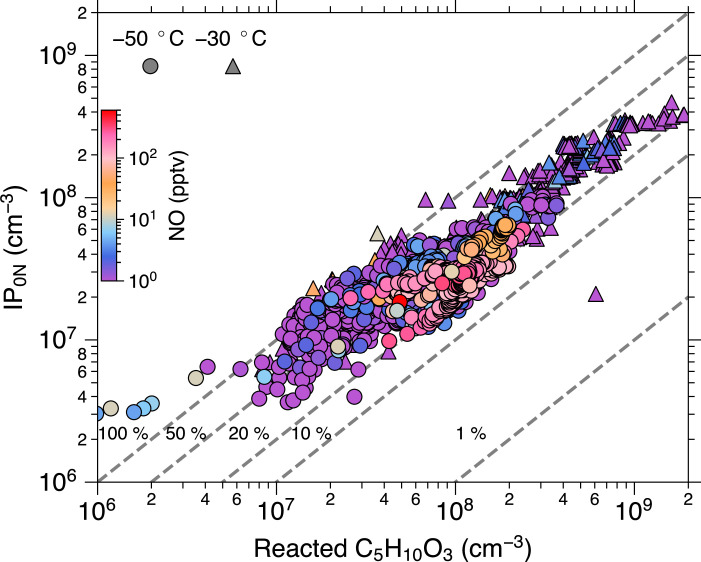
Extended Data Fig. 2. IP0N yield from OH reaction with C5H10O3.
Measured IP0N concentration versus reacted C5H10O3 (see Methods for details). The dashed lines show the predictions for several IP0N molar yields; a yield of 100% implies that each OH reaction with C5H10O3 produces one IP0N molecule. The data indicate that the yield is between 20% and 50%, with an overall systematic uncertainty of a factor of two. When NOx is added to the system, the yield of IP0N is reduced, owing to NO terminating isoprene peroxy radicals. The ratios of IEPOX and ISOPOOH in C5H10O3 are determined from the measured OH concentrations and the fit to the simulation shown in Extended Data Fig. 1b. For simplification, we apply a general reaction-rate coefficient of 10−10 and 10−11 cm3 s−1 for the ISOPOOH + OH and IEPOX + OH reactions, respectively35. The experimental conditions are: isoprene = 0.04–1.50 ppbv (0.1–4.2 × 1010 cm−3), O3 = 1–590 ppbv (3.7 × 1010 to 1.8 × 1013 cm−3), I2 = 0–7.5 × 107 cm−3, SO2 = 0–4.6 × 109 cm−3, OH = 0.11–6.90 × 107 cm−3, HO2 = 0.6–18.0 × 108 cm−3, HO2/OH ratio = 11–117, NO = 0–0.22 ppbv, NO2 = 0–0.77 ppbv, RH = 29–70% and temperature = −30 °C and −50 °C.