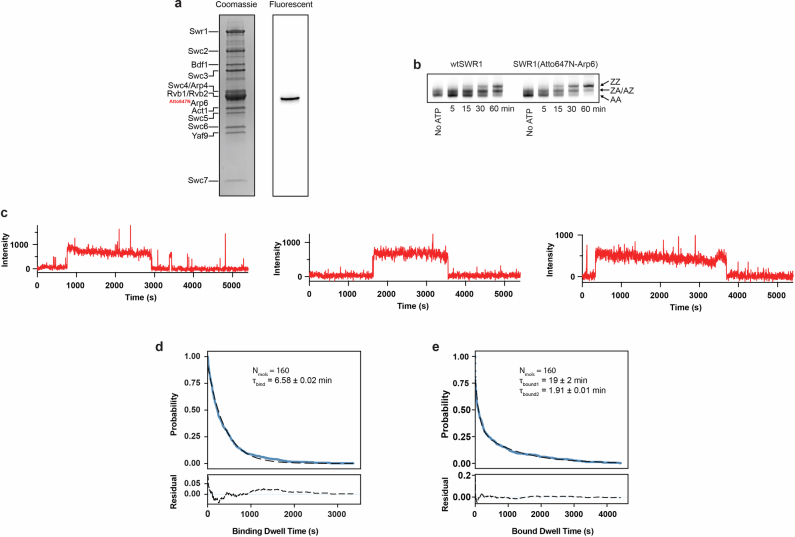
Extended Data Fig. 2. Fluorescently labelled SWR1 and measuring nucleosome bound lifetime.
a, SWR1 was specifically labelled with Atto647N on the N-terminus of the Arp6 subunit. Coomassie stained gel of the purified complex shows the presence of all expected SWR1 subunits (left). The same gel imaged for fluorescence shows that only the Arp6 subunit has been fluorescently labelled (right). Representative gel of three independent preparations. For gel source data, see Supplementary Fig. 1. b, Bulk activity assay using the insertion of a FLAG tagged Htz1–H2B dimer as a readout for exchange. Exchange activity of the labelled SWR1 complex is retained. Representative gel of two independent experiments using enzyme from separate purifications. For gel source data, see Supplementary Fig. 1. c, Three example single molecule intensity trajectories of SWR1(647N) colocalization to surface immobilized nucleosomes. d, Dwell time plot of SWR1(647N) binding times. Data is shown fit to a single exponential decay (with residuals below). On average SWR1 takes 6.58 ± 0.02 min to bind under our experimental conditions. e, Dwell time plot of the lifetime of SWR1(647N) bound to a nucleosome. Data is shown fit to a double exponential decay (with residuals below). Two types of bound complex are present, one stably bound (lifetime 19 ± 2 min) and one more transiently bound (lifetime 1.91 ± 0.01 min). We tentatively assign the transiently bound species to SWR1(647N) interacting with the extranucleosomal DNA, and the stably bound species to SWR1(647N) engaging properly with the nucleosome. Reported errors are the error of the fit.