Fig. 14.
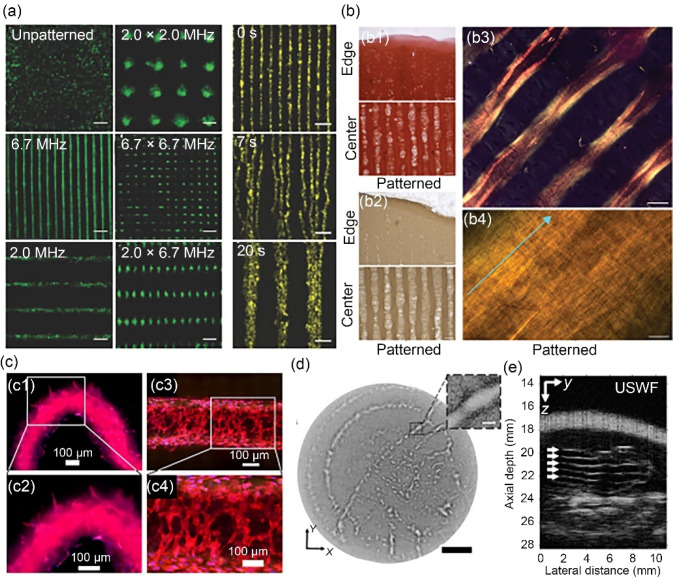
Acoustic cell patterning techniques and applications. a Fluorescence microscopy of acoustically patterned myoblasts, demonstrating the flexibility and rapid dynamic control of ultrasound patterning. Scale bars: 200 µm. Reproduced from Ref. [35], Copyright 2019, with permission from the authors, licensed under CC BY. b Histology showing the deposition of aligned collagen fibres by acoustically-patterned primary bovine articular chondrocytes in agarose: b1 staining for sulfated glycosaminoglycan using safranin O, b2 immunostaining for type II collagen, b3, b4 polarized light microscopy following picrosirius red staining. Scale bars: 100 µm for b1, b2, 50 µm for b3, and 5 µm for b4. Reproduced from Ref. [220], Copyright 2022, with permission from the authors, licensed under CC BY. c Distinct regions of angiogenic sprouting (c1, c2) and cellular network formation (c3, c4) in differentially acoustically patterned regions of RFP-HUVEC-laden bioprinted constructs. Scale bars: 100 µm. Reproduced from Ref. [221], Copyright 2023, with permission from IOP Publishing Ltd. d Acoustic holographic patterning of HCT-116 cells within a collagen hydrogel. Scale bar: 5 mm; inset scale bar: 500 µm. Reproduced from Ref. [223], Copyright 2019, with permission from the authors, licensed under CC BY. e In vivo acoustic patterning of collagen-suspended GFP-HUVECs (reproduced from Ref. [226], Copyright 2023, with permission from the authors, licensed under CC BY 4.0). HUVEC: human umbilical vein endothelial cell; GFP: green fluorescent protein; RFP: red flourescent protein