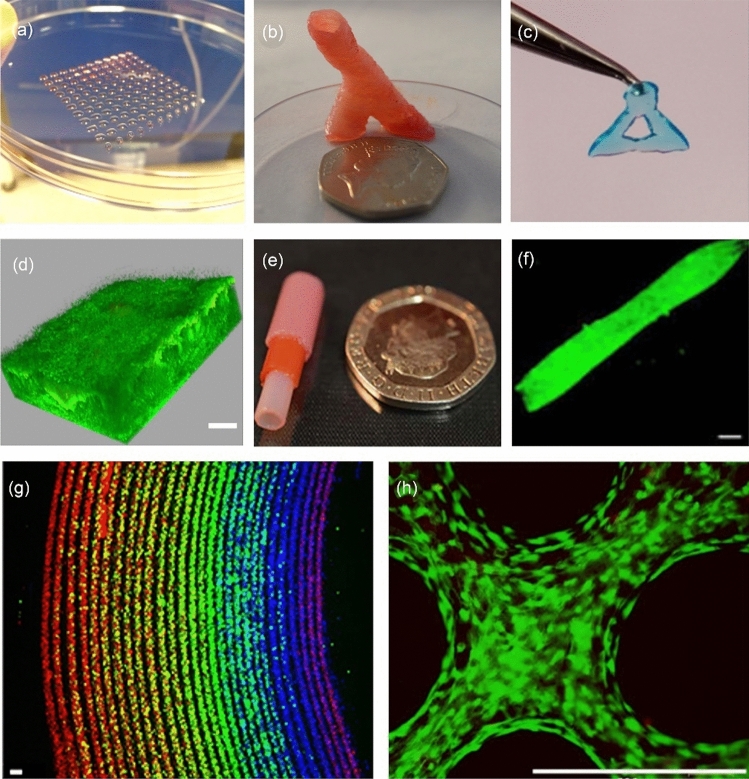
Fig. 15.
Biofabrication research in Shu’s lab: a 3D-bioprinted droplet array of human embryo stem cells (reproduced from Ref. [229], Copyright 2013, with permission from IOP Publishing Ltd); b 3D-printed robust, freestanding alginate hydrogel blood vessel-like structure using secondary (Ca2+) and tertiary (Ba2+) crosslinking steps (scale bar: 20 p coin) (reproduced from Ref. [231], Copyright 2015, with permission from the authors, licensed under CC BY 3.0); c 3D-printed polypeptide-DNA hydrogel with blue dye added for visualisation that is robust enough to be picked up by tweezers (reproduced from Ref. [232], Copyright 2015, with permission from Wiley–VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim); d 3D-reconstructed confocal laser scanning microscope Z-stack of P. aeruginosa biofilm in a 4-mm thick hydrogel construct following 14 days of maturation (scale bar: 100 µm) (reproduced from Ref. [233], Copyright 2019, with permission from the authors, licensed under CC BY 3.0); e multilayered alginate hydrogel tubular structure produced via a micro-dip coating method (scale bar: 20 p coin) (reproduced from Ref. [234], Copyright 2017, with permission from the authors, licensed under CC BY); f fluorescence image of a collagen-organoid tube for transplantable bile duct applications (scale bar: 100 µm) (reproduced from Ref. [236], Copyright 2017, with permission from Nature America, Inc., part of Springer Nature); g confocal image of multilayer prelabelled red, green, and blue high density human embryonic kidney (HEK) cells in a 1% (0.01 g/mL) alginate tube positioned via the rotational internal flow engineering (RIFLE) method (scale bar: 100 µm) (reproduced from Ref. [237], Copyright 2023, with permission from the authors, licensed under CC BY 4.0); h live/dead fluorescent imaging of murine adipose derived stem cells within a micromachined, electrospun polylactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA) fibre mesh (scale bar: 500 µm) (reproduced from Ref. [238], Copyright 2023, with permission from the authors, licensed under CC BY 4.0)