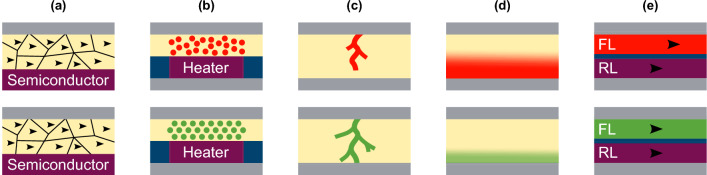
Figure 2.
Schematic illustrations of the working principles of (a) FRAM, (b) PCRAM, (c) filamentary RRAM, (d) area-dependent RRAM, and (e) MRAM. Grey indicates electrodes and pale yellow indicates the memory material. For each, the top schematic represents the high resistance state, and the bottom represents the low-resistance state. The arrows in (a) indicate the ferroelectric polarisation orientation. The dots in (b) indicate the amorphous and crystalline phase of the material. The gradient in (d) indicates the height and width of a Schottky barrier. The arrows in (e) indicate the spin orientation and FL and RL stand for free layer and reference layer, respectively.