Figure 2:
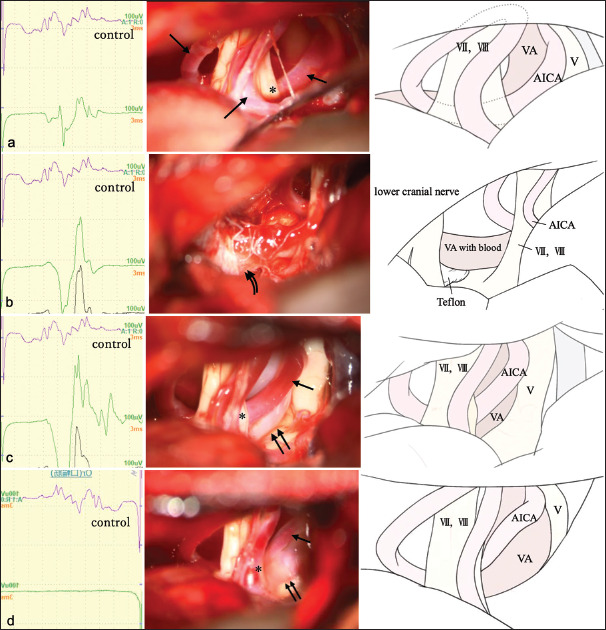
Abnormal muscle response (AMR) waves (left panels), intraoperative photographs (mid), and schematic illustrations (right). (a) Intraoperative findings before microscopic manipulation. The anterior inferior cerebellar artery (AICA) (arrow) on the vertebral artery (VA) is in contact with the facial nerve (asterisk). (b) AMR waves (left panels), intraoperative photographs (mid), and schematic illustrations (right). Teflon felt (curved double arrows) is inserted between the brain stem and VA. AMR is amplified after decompression of the root exit zone. (c) AMR waves (left panels), intraoperative photographs (mid), and schematic illustrations (right). Compression of the facial nerve by AICA (arrow) is exacerbated after further decompression of both sides of the facial nerve (asterisk). AMR is further amplified. (d) AMR waves (left panels), intraoperative photographs (mid), and schematic illustrations (right). Compression of the facial nerve by AICA (arrow) is completely resolved by transposition using fibrin glue (asterisk). AMR remains absent after surgery. double arrows: VA, V: Trigeminal nerve, VII: Facial nerve, VIII:Vestibulocochlear nerve.
