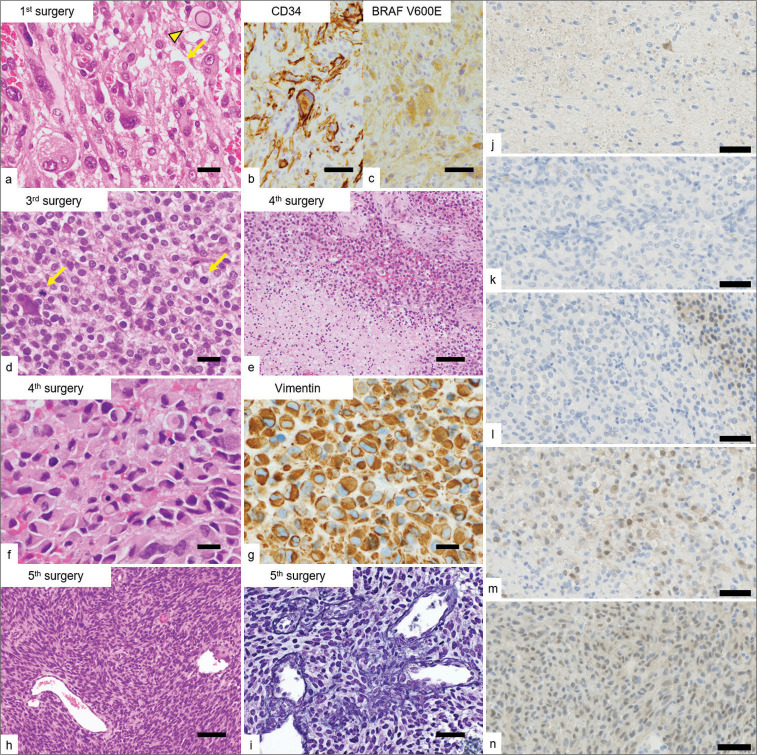
Figure 4:
Microscopic appearances of the resected specimens. (a) The proliferation of pleomorphic and spindle cells with occasional intranuclear pseudo-inclusions (arrowhead) and eosinophilic granular bodies (arrow) in the initially resected specimen. (b and c) Immunohistochemically, the tumor cells were positive for CD34 and BRAF V600E-mutant proteins. (d) The proliferation of tumor cells with epithelioid features showing brisk mitotic activity (arrows) in the recurrent tumor (3rd resection). (e) Coagulative tumor necrosis in the recurrent tumors (4th resection). (f and g) The proliferation of rhabdoid cells with vimentin-positive cytoplasmic inclusions in the recurrent tumors (4th resection). (h) The proliferation of spindle cells in an interlacing fascicular pattern with occasional intervening reticulin fibers in the recurrent tumor, imparts a sarcomatoid appearance (5th resection). (i) Reticulin staining (5th resection). (j-n) ERK1/2 staining (each resection). The ERK1/2 signaling of drug-resistant tumors was expressed strongly despite the presence of the combination therapy with BRAF and MEK inhibitor. (m and n) Scale bars (a, d, f, g) 20 µm, (b, c, i, j, k, l, m, n) 50 µm, and (e, h) 100 µm.