Figure 4. Ventral pallidum inhibition acutely disrupts Pavlovian conditioned alcohol seeking.
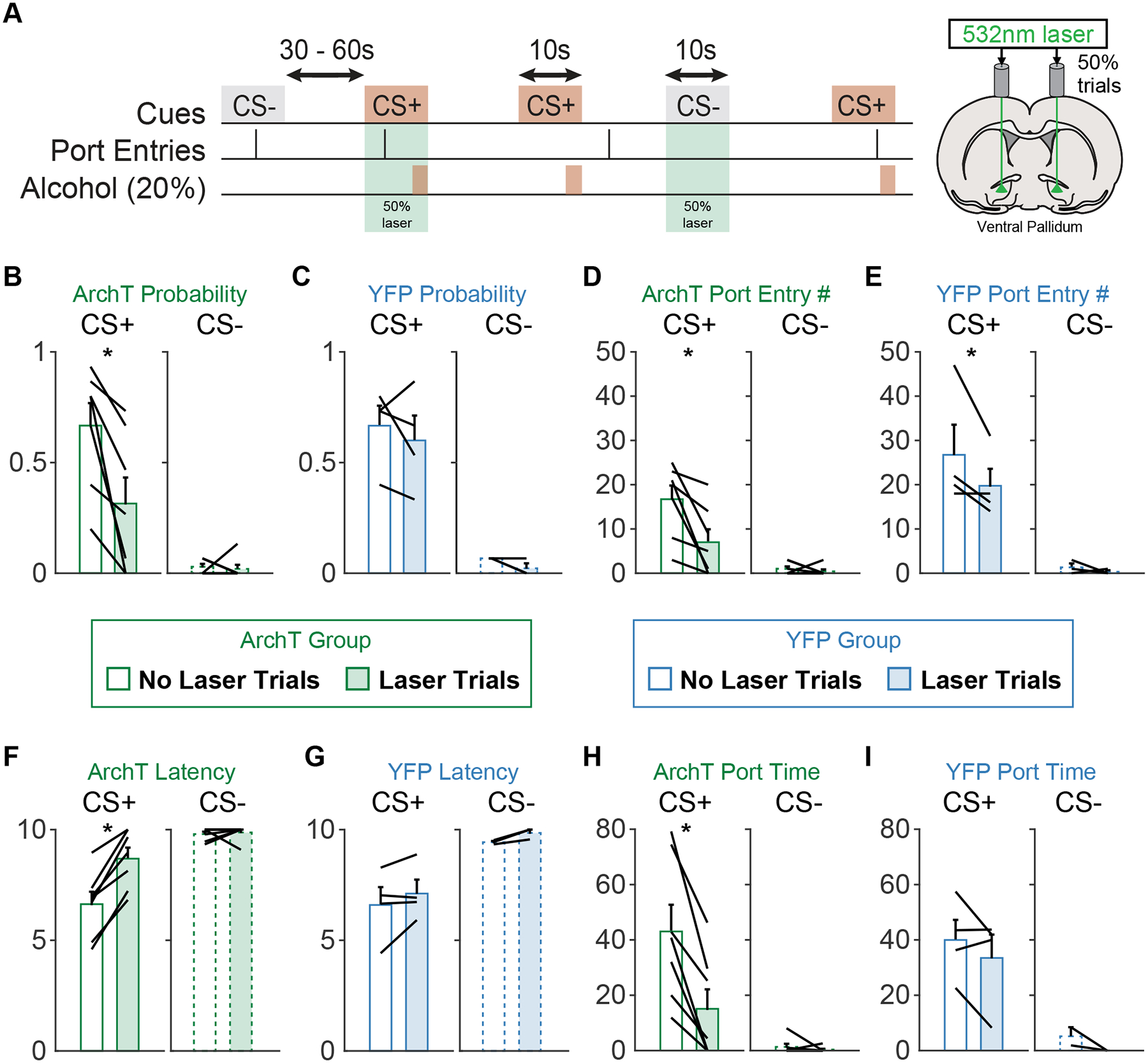
A) Schematic of the optogenetic manipulation. Green laser was delivered on 50% of CS+ and CS− trials. B) Port entry probability during the CS+ was reduced in the ArchT group on laser stimulation trials. C) Port entry probability was not affected by laser delivery in the YFP group. D) The number of port entries during the CS+ was reduced on laser trials for the ArchT group. E) The number of port entries during the CS+ was reduced on laser trials for the YFP group. F) The latency (s) to make port entries during the CS+ was increased on laser trials for the ArchT group. G) There was no effect of laser delivery on port entry latency for the YFP group. H) The time rats spent in the alcohol port (s) during the CS+ was also reduced during laser trials in the ArchT group. I) There was no impact of laser on port entry time for the YFP group.
