Figure 1. Carotid artery plaque images.
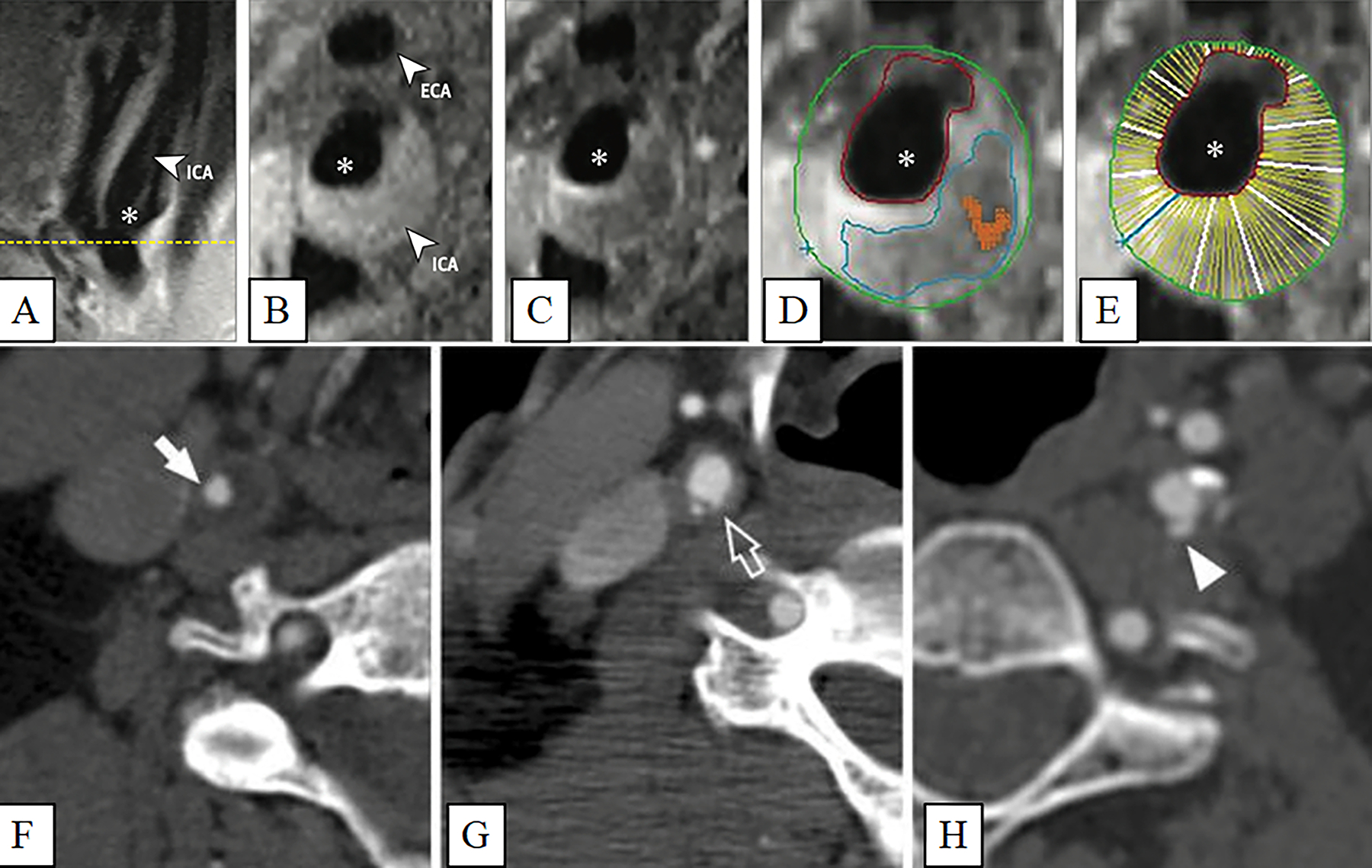
Carotid artery plaque MRI and CT images. Panels A-E: (A) Black blood MRI (BBMRI) images through the carotid artery with atherosclerotic plaque. A long axis BBMRI image through the carotid bifurcation is used for slice positioning. Short axis BBMRI images were then acquired before (B) and after (C) gadolinium contrast administration (asterisk, ICA lumen). Slices shown were acquired at the thickest part of the plaque (yellow line, A). Contours were drawn on the post-contrast image (D) to delineate the lipid core (blue), carotid lumen (red), outer wall (green), and calcification (orange). The wall of the ICA was automatically divided into 12 radial segments (E) to generate thickness measurements. Panels F-H: Various luminal morphology images of carotid artery plaques imaged with CT. (F) Smooth luminal surface (white arrows). (G) Irregular luminal surface (white open arrows). (H) Smooth plaque ulcers (white arrowheads). (Panels A-E: Adapted with permission from: JAMA Cardiol. 2021. 6(1):79–86. Copyright© (2021) American Medical Association. All rights reserved) [14••]. (Panels F-H: Adapted with permission from Springer Nature from: Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 2014, 37(3):572–585. Copyright© 2014) [8].
