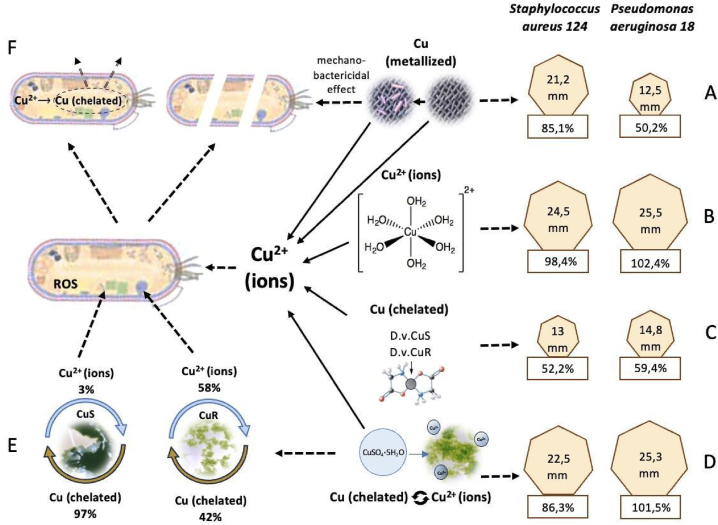
Fig. 10.
Scheme that demonstrates the effectiveness of inhibiting the growth of microorganisms S. aureus 124 and P. aeruginosa 18 when copper in metalized form - A, ionic form - B, was introduced into the bacterial cultures, the effect of components of microalgae D.v-Cu.S and D.v-Cu.R, which contained a small amount of copper (32.2 μg/106 cells) in chelate form - C, the effect of components of the biomass of these microalgae with supplementary added copper sulfate at a concentration of 7 g/l – D, the ratios between the chelate and ionic forms of copper at D.v-Cu.S and D.v-Cu.R - E, as well as a hypothetical mechanism of antibacterial action of copper ions, which demonstrates both the death of most bacteria due to the action on their cell walls and pro-oxidant action of copper ions and possible resistance in a small part of bacteria, which are able to provide effective chelation and its excretion from cells - F.