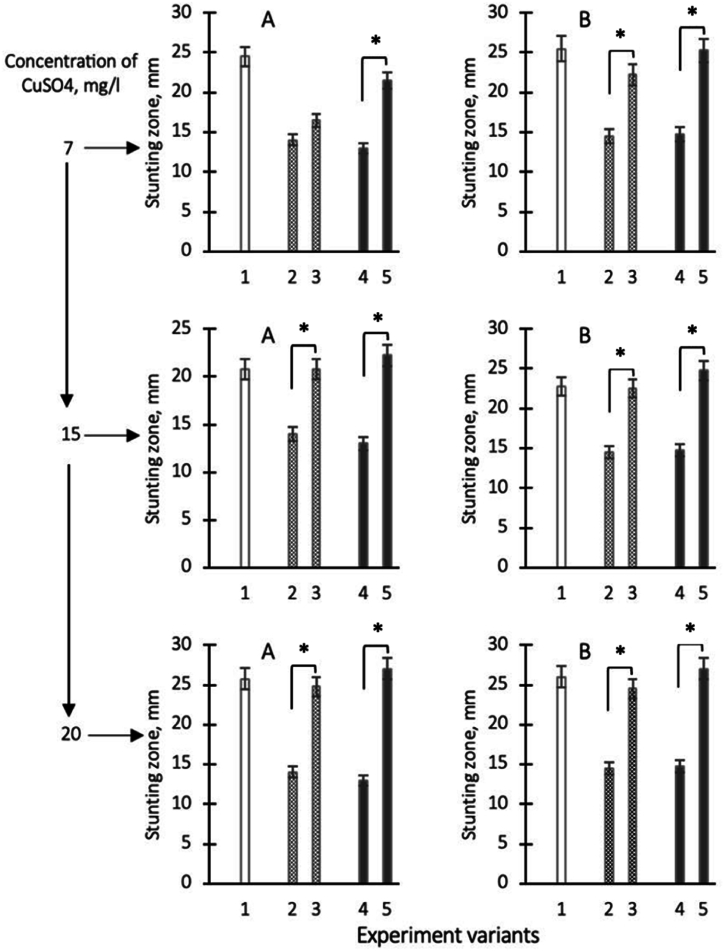
Fig. 5.
Growth inhibition zones of Staphylococcus aureus 124 (A) and Pseudomonas aeruginosa 18 (B) when tested by diffusion (well method) after application of copper sulfate solution (ionic form) at different concentrations: 7; 15 and 20 g/l (shown on an additional scale) respectively they are shown on the ordinate axis as variants 1, variants 2 - zones of growth retardation in case of application of homogenates of D.v-Cu.S cells on discs, which are characterised by the low copper content in chelate form, variants 3 - zones of growth retardation after application of homogenates of D.v-Cu. S with the additional, preliminary introduction of copper sulphoxide into cell homogenates respectively 7; 15, and 20 g/l of copper sulphoxide, variant 4 - zones of growth retardation after application on discs of cell homogenates D.v-Cu. R cells (which initially contained a relatively large amount of copper in the chelate form) and variant 5 - zones of growth retardation after applying homogenates of D.v-Cu.R cells to discs with additional preliminary introduction of 7; 15 and 20 g/l of copper sulfate into homogenates, respectively. The average values from three experiments and their standard errors are presented. ∗ - differences between options 2–3 and 4–5 are significant with P < 0.05.