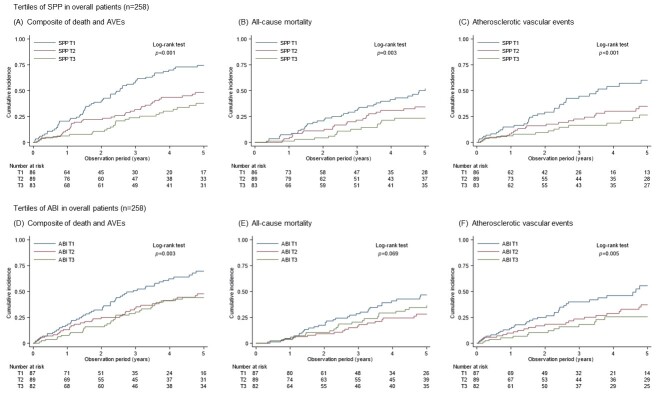
Fig.1. Cumulative incidence of outcomes stratified by SPP and ABI tertiles in all patients.
Kaplan–Meier failure curves show the cumulative incidence of outcomes. In terms of the composite event at the 5-year time point, the tertiles were 0.74, 0.48, and 0.38 for SPP T1, T2, and T3, respectively (p<0.001) (A), and 0.70, 0.48, and 0.44 for ABI T1, T2, and T3 (p=0.003) (D). For all-cause death, the tertiles were 0.52, 0.34, and 0.23, respectively for SPP (p=0.003) (B), and 0.47, 0.28, and 0.36 for ABI (p=0.069) (E). For AVEs, the tertiles were 0.60, 0.35, and 0.27, respectively, for SPP (p<0.001) (C) and 0.56, 0.37, and 0.26 for ABI (p=0.005) (F).
SPP, skin perfusion pressure; ABI, ankle-brachial index; AVEs, atherosclerotic vascular events; T1, 1st tertile; T2, 2nd tertile; T3, 3rd tertile.