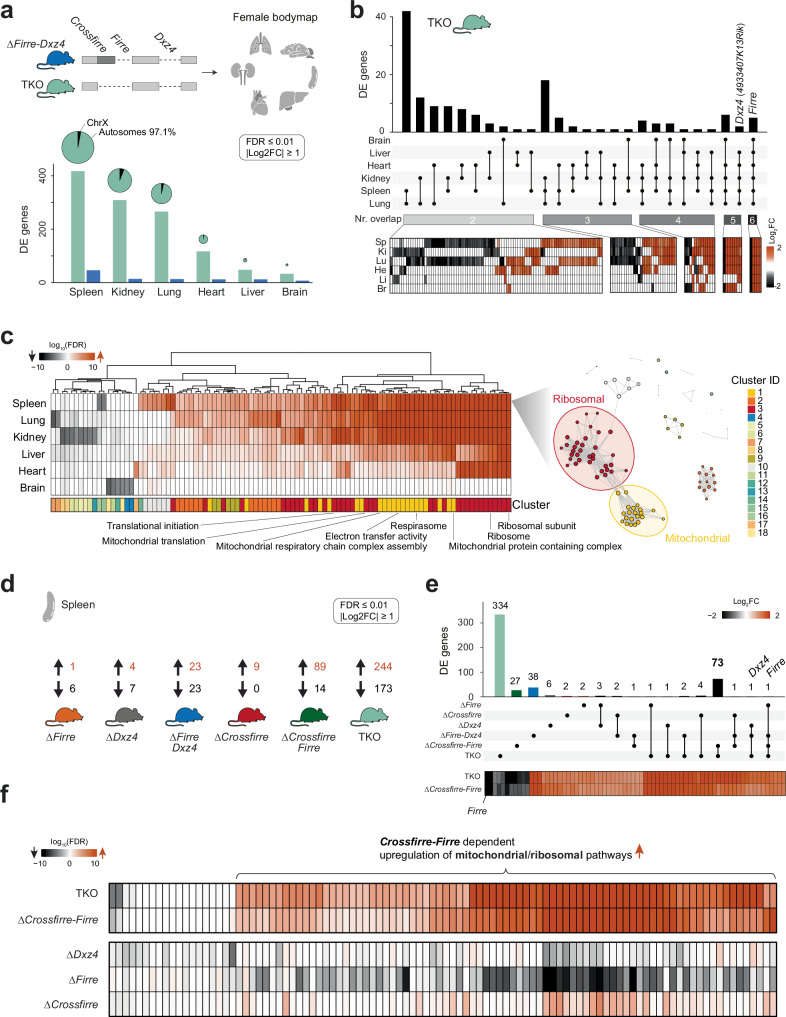
Fig. 5. Homozygous double deletion of Crossfirre-Firre, results in upregulation of mitochondrial and ribosomal pathways.
a Transcriptomic bodymap for six different organs from homozygous adult female ∆Firre-Dxz4 and ∆Crossfirre-Firre-Dxz4 (TKO) mice (wildtype n = 4; ∆Firre-Dxz4 n = 4; TKO n = 3). Chart bars show the number of significantly differentially expressed genes in the spleen, kidney, lung, heart, liver, and brain for TKO and ∆Firre-Dxz4 (DEseq2: FDR ≤ 0.01, |log2FC| ≥ 1). Pie plots represent the proportion of differentially expressed genes between the X chromosome and autosomes as percentages. The size of the pie plots is proportional to the total amount of differentially expressed genes. b Number of differentially expressed genes shared across two, three, four, five, and six different tissues in TKO mice. The heatmap below shows the log2fold changes of the overlapping dysregulated genes per tissue being up- (orange) or downregulated (black). c Heatmap showing the log10(FDR) of the top 100 significantly enriched gene sets from TKO gene set enrichment analysis (left; FDR ≤ 0.1). Network plot for spleen showing 18 gene set clusters with two dominant groups associated with mitochondrial (cluster ID: 1 n = 21) and ribosomal (cluster ID: 3 n = 35) gene sets (right). d Differential gene expression results from RNA-seq data obtained from female spleens of the different knockout strains. The number of significantly up- and downregulated genes is shown per genotype. e Number of significantly differentially expressed genes unique for each genotype and shared by the different knockout models. Below, heatmap showing log2fold changes of differentially expressed genes shared between ∆Crossfirre-Firre and TKO mice. Color shading indicates up- (orange) and downregulation (black). f Gene set enrichment analysis of dysregulated genes from TKO, ∆Crossfirre-Firre, ∆Dxz4, ∆Firre, and ∆Crossfirre deletions. The heatmap shows the log10(FDR) of all informative gene sets of the top 100 significantly enriched gene sets detected in (c).