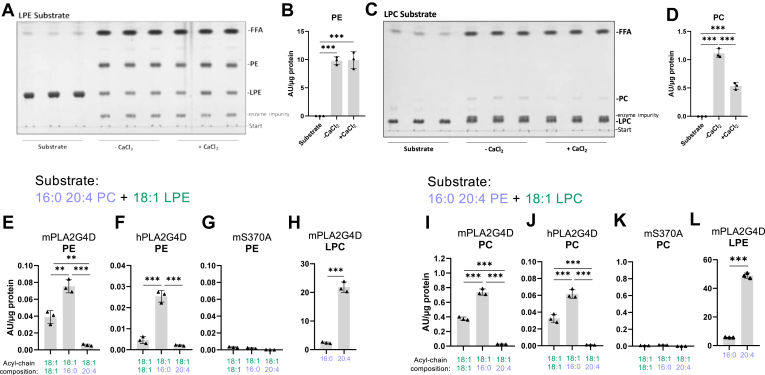
Fig. 2.
PLA2G4D catalyzes the transfer of fatty acids between phospholipids. (A, C) TLC analysis of PLA2G4D-derived reaction products using sn-1-18:1 LPE and sn-1-18:1 LPC as substrates (1 mM) in the absence and presence of 1 mM CaCl2. (B, D) Densitometric quantification of reaction products PE and PC is shown in A and C. (E–L) PLA2G4D-derived reaction products using an equimolar substrate mixture (0.5 mM each) of sn-1-16:0-sn-2-20:4 PC and sn-1-18:1 LPE, or sn-1-16:0-sn-2-20:4 PE and sn-1-18:1 LPC as donor and acceptor, respectively. The mS370A mutant was used as negative control (G, K). Lipids were analyzed by HPLC-MS. PE and PC subspecies are labeled according to their acyl-chain composition. All enzyme activity assays were carried out under conditions described in Figure 1 (n = 3). Data are presented as mean ± SD. Statistical comparison in (H, L) were performed with unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test, and in (B, D, E, F, I, J) with one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni posthoc analysis. Statistically significant differences are shown as: ∗P < 0.05; ∗∗P < 0.01; and ∗∗∗P < 0.001. LPC, lyso-phosphatidylcholine; LPE, lyso-phosphatidylethanolamine; PC, phosphatidylcholine; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine; PLA2G4, phospholipase A2 group IV.