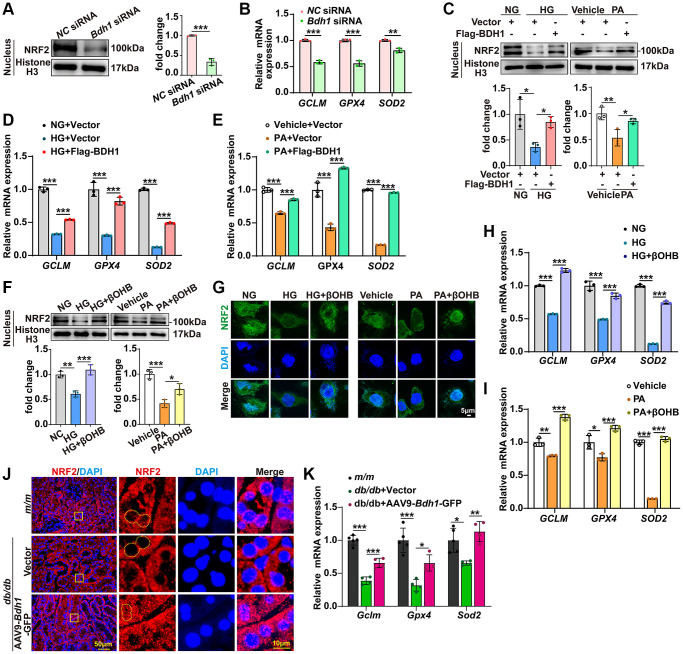
Figure 4.
BDH1-mediated βOHB metabolism promotes NRF2 nuclear translocation. (A) Representative WB image showing the protein level of NRF2 protein in the nuclear translocation of HK-2 cells transfected with NC siRNA or Bdh1 siRNA. (B) mRNA expression of GCLM, GPX4, and SOD2 in HK-2 cells transfected with NC siRNA or Bdh1 siRNA. (C) Representative WB images showing the protein level of NRF2 in the nuclear translocation of BDH1-overexpressed HK-2 cells treated with HG or PA. (D, E) mRNA expression of GCLM, GPX4, and SOD2 in BDH1-overexpressed HK-2 cells stimulated with HG (D) or PA (E). (F) Representative WB images showing the protein level of NRF2 in the nuclear translocation of βOHB-supplemented HK-2 cells treated with HG or PA. (G) Representative IF images showing the location of NRF2 in βOHB-supplemented HK-2 cells treated with HG or PA. (H, I) The mRNA expression of GCLM, GPX4, and SOD2 in βOHB-supplemented HK-2 cells stimulated with HG (H) or PA (I). (J) Representative IF images showing the location of NRF2 in kidneys of indicated groups. (K) mRNA levels of Gclm, Gpx4, and Sod2 in the kidneys of m/m group (n = 5), db/db + Vector (n = 4), and db/db + AAV-Bdh1-GFP group (n = 4). All results are representative of three independent experiments. Values are presented as mean ± standard deviation. Bar: 5 μm in G, 50 μm and 10 μm in J. Abbreviations: BDH1: β-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase 1; βOHB: β-hydroxybutyrate; WB: western blot; HG: high glucose; PA: palmitic acid; IF: immunofluorescence. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.