Figure 1.
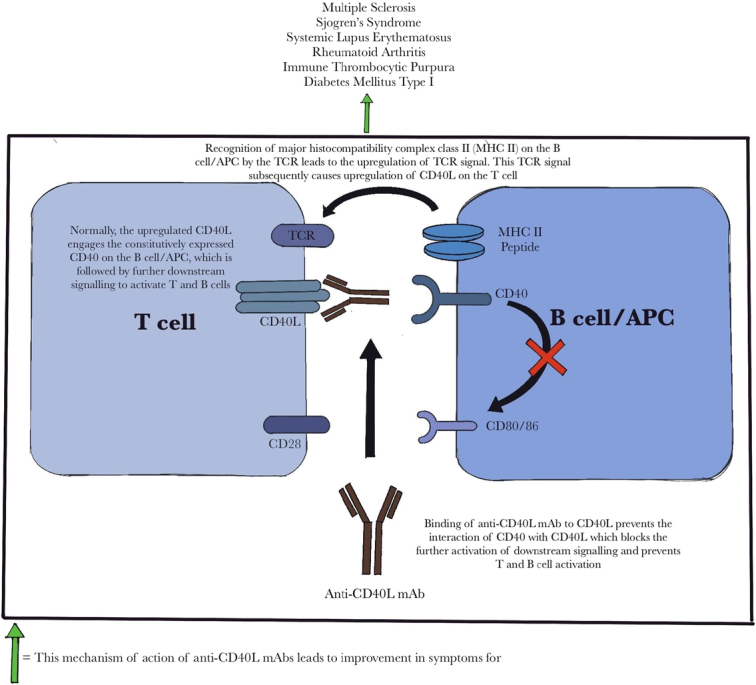
The figure demonstrates the proposed mechanism of action of anti-CD40L monoclonal antibodies and how they further contribute towards the amelioration of symptoms in various autoimmune disorders. Normally, activation of T cells by antigen-presenting cells (APCs)/B cells requires the interaction of costimulatory molecules and the subsequent activation of the T cell receptor (TCR) signal. Anti-CD40L mAbs prevent this interaction and the downstream signaling. APC, antigen presenting cell; TCR, T-cell receptor; MHC II, major histocompatibility complex class II; mAb, monoclonal antibody.
