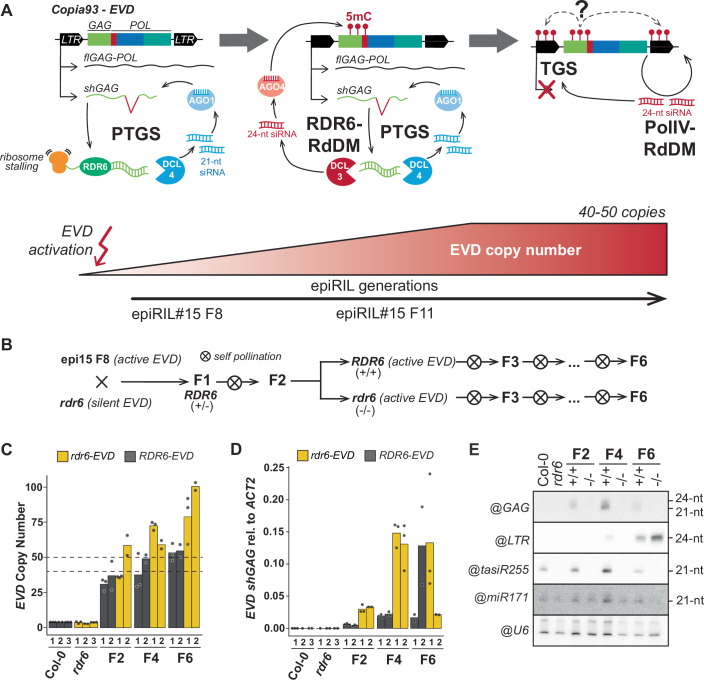
Figure 1. Introgression and characterization of EVD in the rdr6 mutant background.
(A) Schematic representation of the three EVD silencing steps. Upon EVD reactivation, ribosome stalling during translation of EVD shGAG transcript triggers PTGS. 21-nt siRNA produced through RDR6 and DCL4 and loaded into AGO1. With increasing EVD copies across generations, the excess of dsRNA produced by RDR6 is processed by DCL3 to generate 24-nt siRNAs. Loaded into AGO4, shGAG siRNAs trigger DNA methylation (5mC) through RDR6-RdDM at GAG coding sequences without silencing. At 40–50 copies per genome, TGS is installed through Pol IV-RdDM, coincidentally with the appearance of DNA methylation and 24-nt siRNAs on the LTR sequences. (B) Crossing scheme to generate rdr6 mutant lines with active EVD. F2 plants were genotyped to select homozygous WT and mutant RDR6 lines, propagated through selfing until the F6 generation. (C) EVD copy number analysis by qPCR in RDR6-EVD and rdr6-EVD lines at generations F2, F4, and F6 derived from two independent F1s (biological replicates), using the EVD-GAG sequence as target. (D) qPCR analysis of shGAG expression normalized to ACT2 in EVD-RDR6 and EVD-rdr6 lines at generations 2, 4, and 6 derived from two independent F1s (biological replicates). In (C) and (D), each biological replicate, consistent of bulks of 8–10 plants, are represented for each genotype at each generation, dots show technical replicates. (E) RNA blot analysis of EVD siRNAs against GAG and LTR in RDR6 and rdr6 lines with active EVD at generations F2, F4, and F6. tasiR255 probe is used as control for RDR6 mutation, miR171 and snoRNA U6 are shown as loading controls. WT Col-0 and rdr6 with no reactivated EVD are shown as negative control for EVD activity. Source data are available online for this figure.