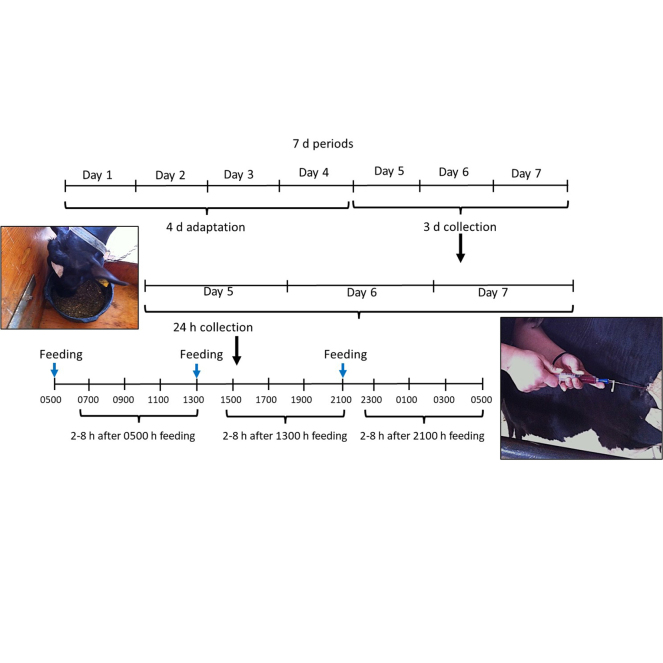
Summary: Estimating the relative bioavailability of rumen-protected (RP) amino acid supplements using the plasma free amino acid dose-response methodology currently uses blood collected at 2, 4, 6, and 8 hours after the 0500 hour feeding over 3 days, with cows being fed every 8 hours (0500, 1300, and 2100 hours). We conducted a study where blood samples were collected at 2, 4, 6, and 8 hours after each of the feedings to investigate whether this sampling protocol captures the diurnal changes in plasma methionine (Met) concentrations that may exist to adequately calculate the relative bioavailability of Met from RP-Met supplements. There was no diurnal variation in plasma Met concentration, and the relative bioavailability calculated for the RP-Met supplement tested did not differ significantly, thus indicating that the proposed sampling protocol can be used to determine the relative bioavailability of RP-Met supplements.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.