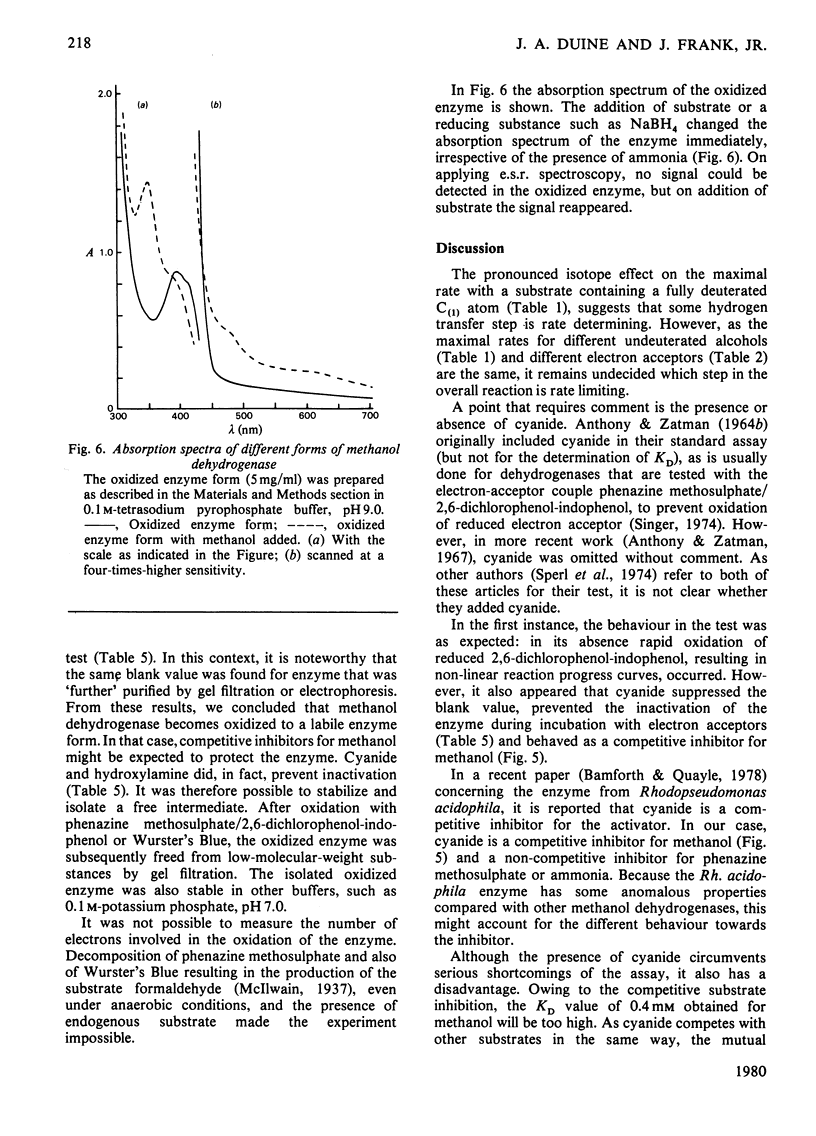
Abstract
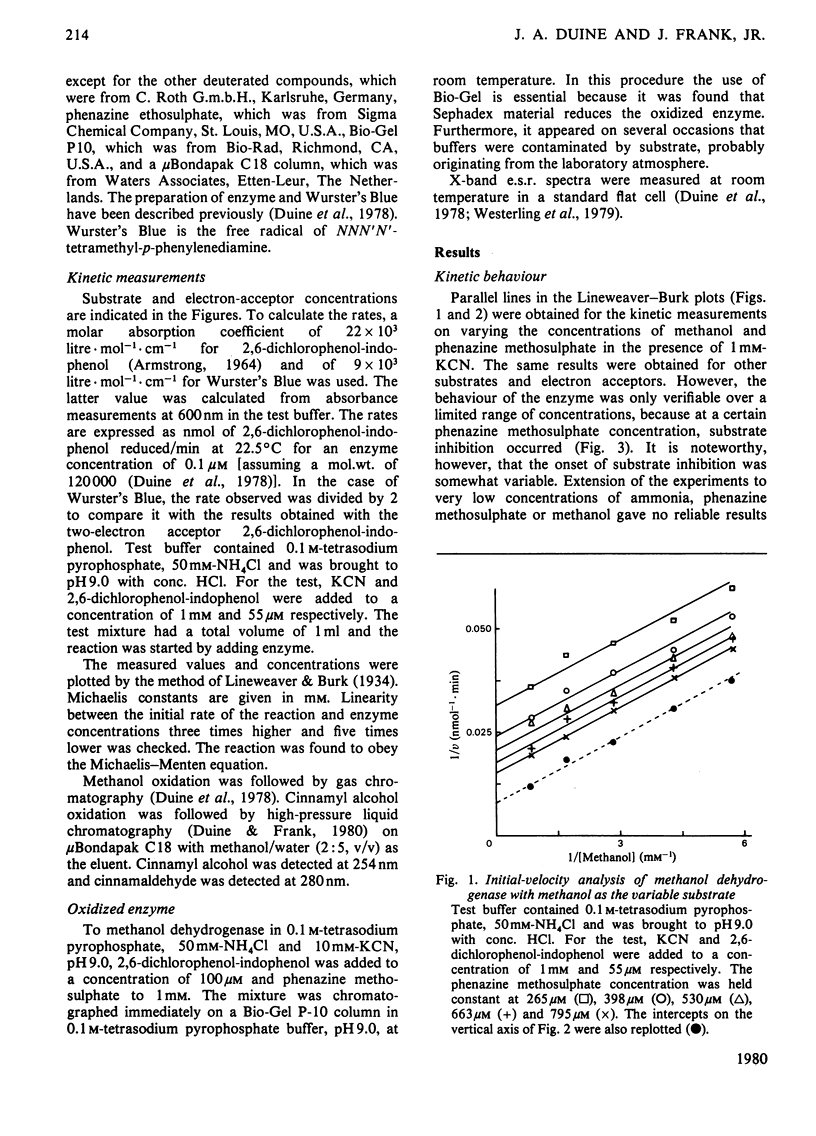
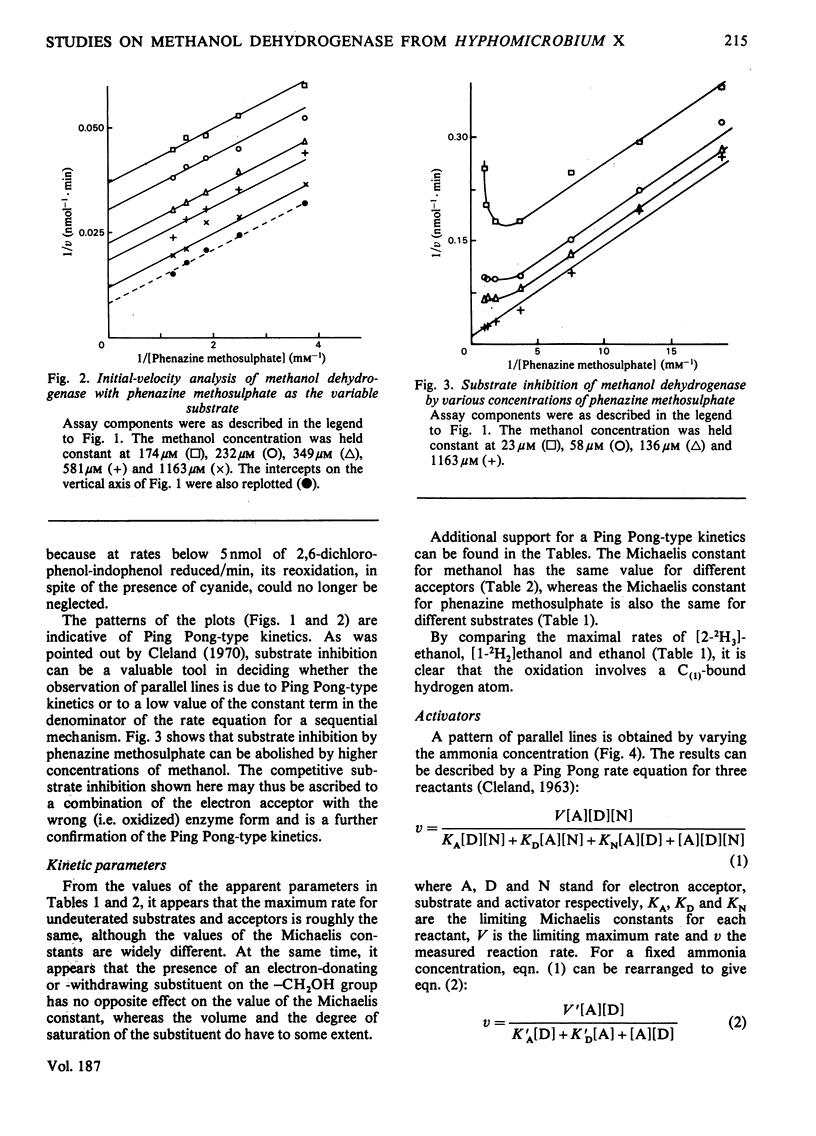
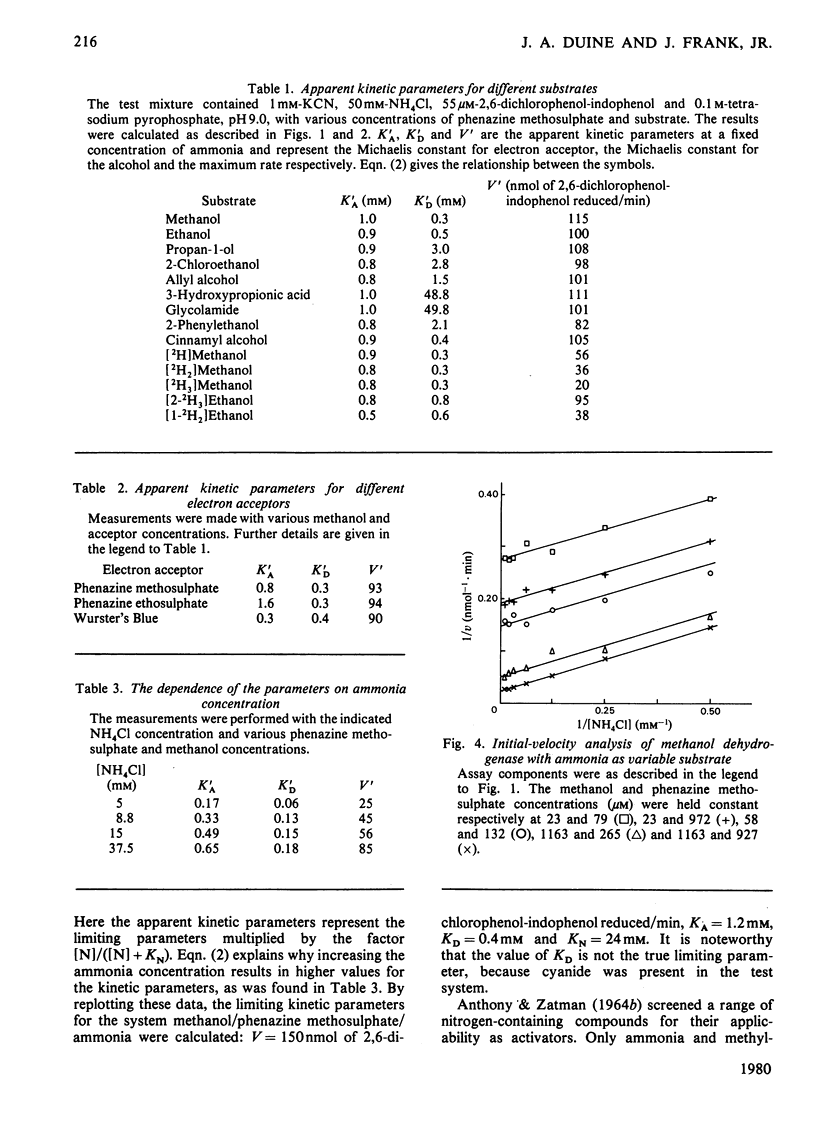
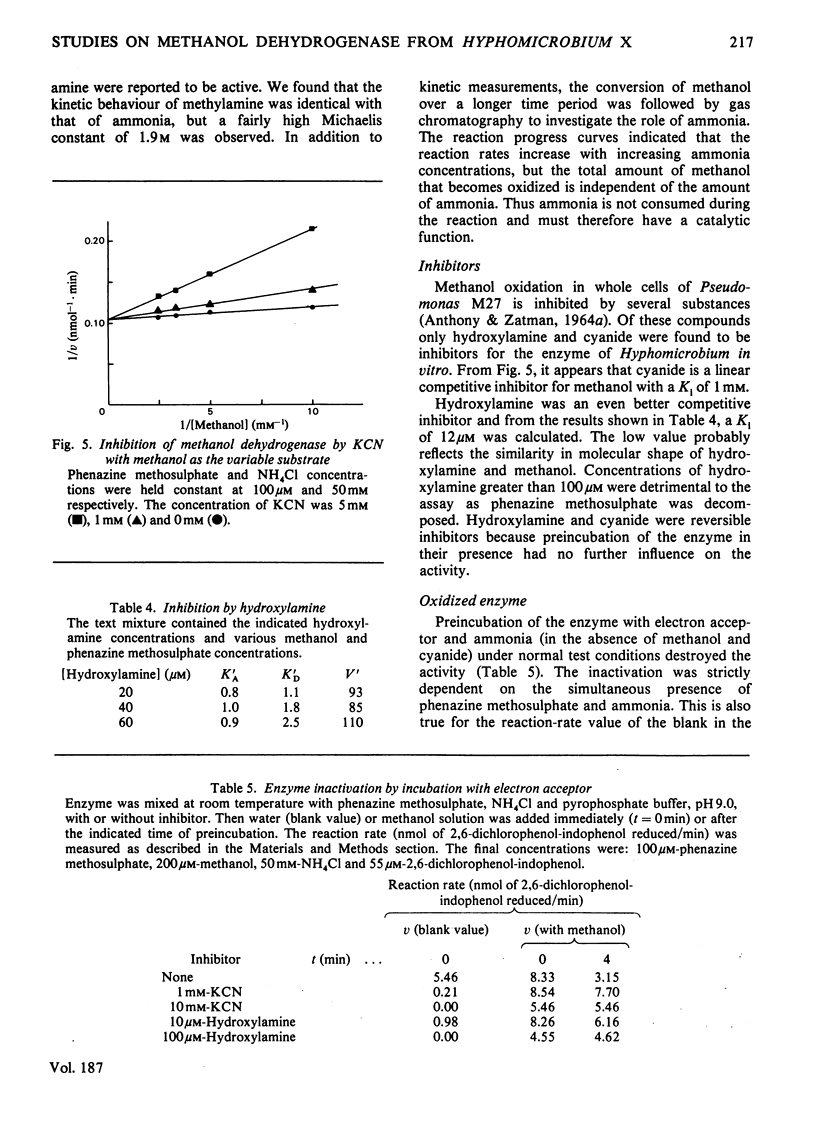
1. Double-reciprocal plots of initial reaction rates of methanol dehydrogenase [alcohol--(acceptor) oxidoreductase, EC 1.1.99.8] in vitro show patterns of parallel lines. The results with various methanol, ammonia and phenazine methosulphate concentrations can be described by an equation valid for a Ping Pong kinetic mechanism with three reactants. 2. The overall maximum velocity was the same for several primary alcohols, C(2)-deuterated ethanols and different electron acceptors, but it was significantly lower for C(1)-deuterated substrates. 3. Oxidation of the isolated enzyme with electron acceptors required the presence of ammonia and a high pH. The inclusion of cyanide or hydroxylamine during the incubation was essential to prevent enzyme inactivation. The absorbance spectrum of an oxidized form of the enzyme was clearly different from that of the isolated enzyme and the free radical was no longer present. On addition of substrate, the original absorption spectrum and electron-spin-resonance signal reappeared and a concomitant substrate oxidation was found. This reaction could be carried out at pH 7 and ammonia was not required. 4. Based on the activity of the enzyme with one-electron acceptors, the presence of a free radical and the kinetic behaviour, an oxidation of the enzyme via one-electron steps is proposed.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARMSTRONG J. M. THE MOLAR EXTINCTION COEFFICIENT OF 2,6-DICHLOROPHENOL INDOPHENOL. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Apr 4;86:194–197. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(64)90180-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anthony C., Zatman L. J. The microbial oxidation of methanol. 1. Isolation and properties of Pseudomonas sp. M27. Biochem J. 1964 Sep;92(3):609–614. doi: 10.1042/bj0920609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anthony C., Zatman L. J. The microbial oxidation of methanol. 2. The methanol-oxidizing enzyme of Pseudomonas sp. M 27. Biochem J. 1964 Sep;92(3):614–621. doi: 10.1042/bj0920614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anthony C., Zatman L. J. The microbial oxidation of methanol. Purification and properties of the alcohol dehydrogenase of Pseudomonas sp. M27. Biochem J. 1967 Sep;104(3):953–959. doi: 10.1042/bj1040953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bamforth C. W., Quayle J. R. The dye-linked alcohol dehydrogenase of Rhodopseudomonas acidophila. Comparison with dye-linked methanol dehydrogenases. Biochem J. 1978 Mar 1;169(3):677–686. doi: 10.1042/bj1690677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLELAND W. W. The kinetics of enzyme-catalyzed reactions with two or more substrates or products. I. Nomenclature and rate equations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Jan 8;67:104–137. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91800-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duine J. A., Frank J., Jr The prosthetic group of methanol dehydrogenase. Purification and some of its properties. Biochem J. 1980 Apr 1;187(1):221–226. doi: 10.1042/bj1870221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duine J. A., Frank J., Westerling J. Purification and properties of methanol dehydrogenase from Hyphomicrobium x. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jun 9;524(2):277–287. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(78)90164-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg I. Purification and properties of a methanol-oxidizing enzyme in Pseudomonas C. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Mar 16;63(1):233–240. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10225.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer T. P. Determination of the activity of succinate, NADH, choline, and alpha-glycerophosphate dehydrogenases. Methods Biochem Anal. 1974;22:123–175. doi: 10.1002/9780470110423.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperl G. T., Forrest H. S., Gibson D. T. Substrate specificity of the purified primary alcohol dehydrogenases from methanol-oxidizing bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1974 May;118(2):541–550. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.2.541-550.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westerling J., Frank J., Duine J. A. The prosthetic group of methanol dehydrogenase from Hyphomicrobium X: electron spin resonance evidence for a quinone structure. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Apr 13;87(3):719–724. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)92018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


