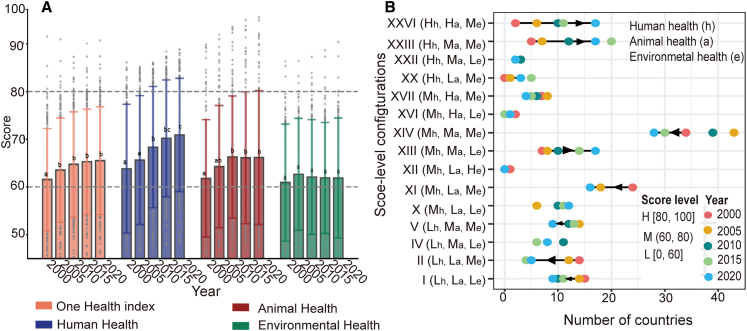
Figure 1.
Global One Health progressed and changed in the number of countries with three configurations of scores for human, animal, and environmental health worldwide from 2000 to 2020
(A) Global annual average score of the One Health index, human, animal, and environmental health, from 2000 to 2020. The bar height represents the mean. The upper bound is defined as Q3 + 1.5 ∗ IQR, while the lower bound is Q1 − 1.5 ∗ IQR, where Q1 and Q3 are the 25th and 75th percentiles, respectively, and IQR is the interquartile range for the sample of 148 countries (n = 148).
(B) Countries were grouped into 15 configurations of score levels for human (h), animal (a), and environmental health (e) (see STAR Methods, Table S3). Those with scores ≥80 are performing well (H), those with scores ≤60 are facing substantial challenges (L), and those with scores between 60 and 80 are performing moderately (M).