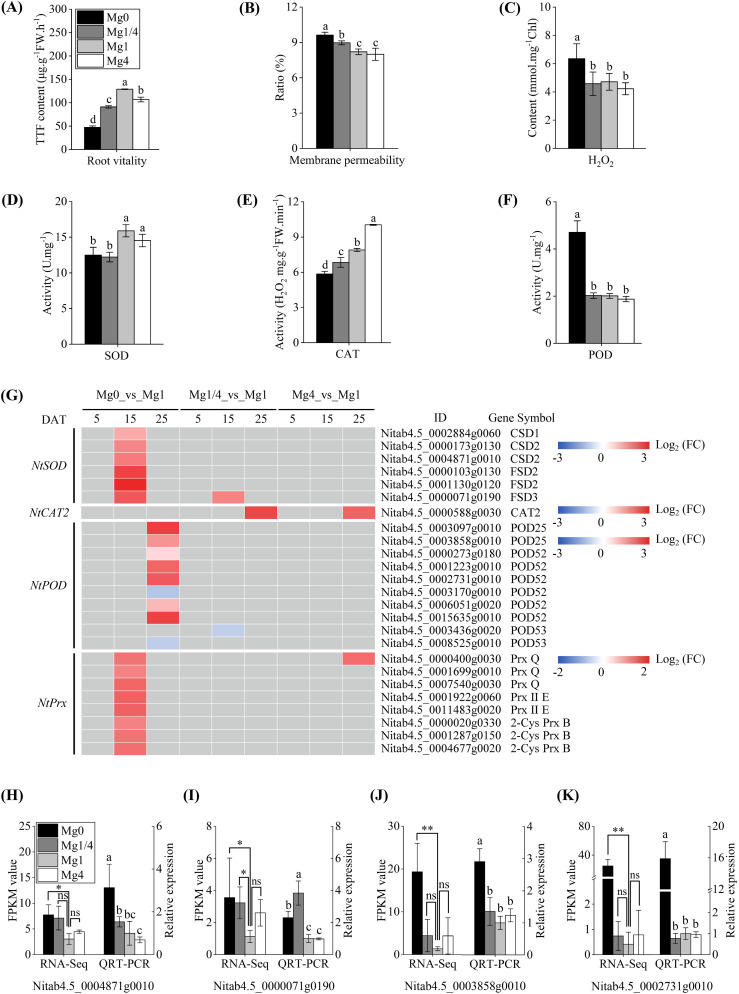
Figure 7.
Effects of different Mg supplies on physiological parameters related to antioxidant defense and expressional changes of key DEGs involved in enzymatic scavenging. (A-C) Root vitality, Cell membrane permeability, and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) content, respectively, in leaves of tobacco seedlings grown under different Mg supplies at 25 DAT. (D-F) Activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and peroxidase (POD) in leaves of tobacco seedlings grown under different Mg supplies at 25 DAT. (G) Heatmap showing the differential expression levels of SOD, CAT2, POD, and peroxiredoxin (Prx) family DEGs, respectively. Grey blocks indicate that the genes were not detected as DEGs by RNA-Seq. (H-K) qRT-PCR validation of two DEGs NtCSD2 (Nitab4.5_0004871g0010) and NtFSD3 (Nitab4.5_0000071g0190) in the Mg0, Mg1/4, Mg1, and Mg4 seedlings at 15 DAT, and two DEGs NtPOD25 (Nitab4.5_0003858g0010) and NtPOD52 (Nitab4.5_0002731g0010) in the Mg0, Mg1/4, Mg1, and Mg4 seedlings at 25 DAT. The tobacco EF-1α gene was used as an internal control. Mg0, 0 mM Mg; Mg1/4, 0.50 mM Mg; Mg1, 1.99 mM Mg; Mg4, 7.96 mM Mg. DAT, days after treatment. Significance levels *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ns, not significant. Different letters (a, b, c, d) above the columns indicate statistical differences (p < 0.05).